Международный неврологический журнал 7 (77) 2015
Вернуться к номеру
Современные возможности магнитно-резонансной томографии у преждевременно рожденных детей
Авторы: Мартыненко Я.А. - ГУ «Институт педиатрии, акушерства и гинекологии НАМН Украины», г. Киев; Херсонская областная детская клиническая больница Херсонского областного совета; Медицинский центр физической терапии и боли INNOVO, г. Львов
Рубрики: Неврология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Найбільші темпи розвитку головного мозку припадають на третій триместр вагітності та перші місяці після народження. Передчасно народжені діти мають великий ризик ураження головного мозку. Нейровізуалізація відіграє значну роль у встановленні діагнозу та виходжуванні недоношених дітей. Як нейросонографія, так і магнітно-резонансна томографія (МРТ) відзначаються специфічністю та чутливістю до встановлення пошкоджень головного мозку. МРТ не використовується як скринінговий метод, але може забезпечити фахівців високою діагностичною та прогностичною інформацією. Сьогодні, окрім стандартного МРТ-дослідження, доступні такі методики, як дифузійно-тензорна томографія і трактографія, магнітно-резонансна спектроскопія, функціональна магнітно-резонансна томографія, волюмометричні дослідження, автоматичні сегментації головного мозку. Комбіноване використання звичайних і новітніх методів МРТ дозволяє своєчасно визначити маркери патологічного розвитку дитини та заходи з метою зменшення клінічних проявів.
Наибольшие темпы развития головного мозга приходятся на третий триместр беременности и первые месяцы после рождения. Преждевременно рожденные дети имеют большой риск развития повреждений головного мозга. Нейровизуализация играет значительную роль в установлении диагноза и выхаживании недоношенных детей. Как нейросонография, так и магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ) обладают специфичностью и чувствительностью верификации повреждений головного мозга. МРТ не используется как скрининговый метод, но может обеспечивать специалистов высокой диагностической и прогностической информацией. Сегодня, кроме стандартного МРТ-исследования, доступны такие методики, как диффузно-тензорная томография и трактография, магнитно-резонансная спектроскопия, функциональная магнитно-резонансная томография, волюметрические исследования, автоматическая сегментация головного мозга. Комбинированное использование обычных и новейших методов МРТ позволяет своевременно определить маркеры патологического развития ребенка и меры с целью уменьшения клинических проявлений.
The last trimester of fetal development extending into the first post-natal months is a period of the most rapid brain development. Infants who are born premature have high risk of brain injury. Neuroimaging has played an important role in the diagnosis and nursing of preterm infants. Both neurosonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are characterized by specificity and sensitivity enough to establish brain damage. MRI is not used as a screening method, but can provide specialists with high diagnostic and prognostic information. To date, in addition to a standard MRI, such techniques as diffusion tensor imaging and tractography, magnetic resonance spectroscopy, functional magnetic resonance imaging, volumetric studies, automatic segmentation of the brain are available. The combined use of conventional and advanced MRI techniques enables to determine timely the markers of the pathological child development and activities to reduce clinical manifestations.
екстремально низька маса тіла, недоношеність, магнітно-резонансна томографія, нейровізуалізація.
экстремально низкая масса тела, недоношенность, магнитно-резонансная томография, нейровизуализация.
extremely low birth weight, prematurity, magnetic resonance imaging, neuroimaging.
Статтю опубліковано на с. 42-51
Актуальність
Методи нейровізуалізації
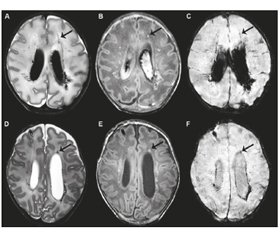
Внутрішньошлуночкові крововиливи
/44.jpg)
Вентрикулодилатація
Патологія білої речовини головного мозку
Дифузна гіперінтенсивність білої речовини головного мозку (diffuse excessive high signal intensities, DEHSI)
/46.jpg)
Патологія сірої речовини головного мозку
Мозочкові ураження
/47.jpg)
Класифікація патологічних уражень головного мозку у передчасно народжених дітей за даними МРТ головного мозку
Терміни проведення МРТ
1. Аряев Н.Л. Реалии и перспективы выхаживания детей с экстремально низкой массой тела при рождении в мире и в Украине / Н.Л. Аряев, Н.В. Котова // Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина. — 2011. — Т. 1, № 1 — С. 101-107.
2. Знаменская Т.К. Основные проблемы и направления развития неонатологии на современном этапе развития медицинской помощи в Украине / Т.К. Знаменская // Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина. — 2011. — Т. 1, № 1 — С. 5-9.
3. Знаменська Т.К. Діагностика гіпоксично-ішемічного ураження головного мозку у недоношених дітей / Т.К. Знаменська, Л.Г. Кирилова, В.Б. Швейкіна // Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина. — 2013. — Т. 3, № 2(8). — С. 31-39.
4. Пальчик А.Б. Неврология недоношенных детей / А.Б. Пальчик, Л.А. Федорова, А.Е. Понятишин. — М.: МЕДпресс-информ, 2010. — 352 с.
5. Шунько Є.Є. Впровадження концепції подальшого розвитку перинатальної допомоги в Україні / Є.Є. Шунько // Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина. — 2011. — Т. 1, № 1. — С. 10-16.
6. Шунько Є.Є. Стратегія розвитку та наукові напрямки неонатології та педіатрії в Україні / Є.Є. Шунько // Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина. — 2014. — Т. 4, № 3. — С. 11-14.
7. Яблонь О.С. Наш досвід у вирішенні проблемних питань збереження життя і здоров’я надзвичайно недоношених немовлят / О.С. Яблонь, Д.Ю. Власенко, Т.І Антонець та ін. // Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина. — 2013. — Т. 3, № 2(8). — С. 25-30.
8. Ancel P. Survival and morbidity of preterm children born at 22 through 34 weeks’ gestation in France in 2011: results of the EPIPAGE-2 cohort study / P.Y. Ancel, F. Goffinet, P. Kuhn et al. // JAMA Pediatr. — 2015. — Vol. 69(3). — P. 230-238.
9. Arichi T. Brain development in preterm infants assessed using advanced MRI techniques / T. Arichi, D. Edwards, S. Counsell et al. // Clin. Perinatol. — 2014. — Vol. 41. — P. 25-45.
10. Arthurs O. The challenges of neonatal magnetic resonance / O. Arthurs, A. Edwards, T. Austin et al. // Pediatr. Radiol. — 2012. — Vol. 42. — P. 1183-1194.
11. Austin T. Advances in imaging the neonatal brain / T. Austin, H. O’Reilly // Expert. Opin. Med. Diagn. — 2011. — Vol. 5. — P. 95-107.
12. Back S. Cerebral white and gray matter injury in newborns: new insights into pathophysiology and management / S. Back // Clin. Perinatol. — 2014. — Vol. 41(1) — P. 1-24.
13. Ball G. The Effect of preterm birth on thalamic and cortical development / G. Ball, J. Boardman, D. Rueckert et al. // Cerebral. Cortex. — 2012. — Vol. 22. — P. 1016-1024.
14. Ball G. Thalamocortical connectivity predicts cognition in children born preterm / G. Ball, L. Pazderova, A. Chew et al. // Cerebral. Cortex. — Jan 16, 2015. — pii: bhu331.
15. Bassi L. Diffusion tensor imaging in preterm infants with punctuate white matter lesions / L. Bassi, A. Chew, N. Merchant et al. // Pediatric. Research. — 2011. — Vol. 69(6). — P. 561-566.
16. Beaino G. Predictors of cerebral palsy in very preterm infants: the EPIPAGE prospective population-based cohort study / G. Beaino, B. Khoshnood, M. Kaminski et al. // Dev. Med. Child Neurol. — 2010. — Vol. 52. — e119-e125.
17. Blencowe H. Born too soon: the global epidemiology of 15 million preterm births / H. Blencowe, S. Cousens, D. Chou et al. // Reprod. Health. — 2013. — Vol. 10, Suppl. 1. — 2.
18. Boardman J. A common neonatal image phenotype predicts adverse neurodevelopmental outcome in children born preterm / J. Boardman, C. Craven, S. Valappil et al. // Neuroimage. — 2010. — Vol. 52(2). — P. 409-414.
19. Bonifacio S. Extreme premature birth is not associated with impaired development of brain microstructure / S. Bonifacio, H. Glass, V. Chau et al. // J. Pediatr. — 2010. — Vol. 157(5). — P. 726-732.
20. de Bruine F. Clinical implications of MR imaging findings in the white matter in very preterm infants: a 2-year follow-up study / F. de Bruine, A. den Berg-Huysmans, L. Leijser et al. // Radio–logy. — 2011. — Vol. 261(3). — P. 899-906.
21. Brouwer M. Sequential cranial ultrasound and cerebellar diffusion weighted imaging contribute to the early prognosis of neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants / M. Brouwer, B. van Kooij, I. van Haastert et al. // PLoS One. — 2014. — Vol. 9(10). — e109556.
22. Cornette L. Magnetic resonance imaging of the infant brain: anatomical characteristics and clinical significance of punctate lesions / L. Cornette, S. Tanner, L. Ramenghi et al. // Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. — 2002. — Vol. 86. — F 171-F 177.
23. Dean J. Prenatal cerebral ischemia disrupts MRI-defined cortical microstructure through disturbances in neuronal arborization / J. Dean, E. McClendon, K. Hansen et al. // Sci. Transl. Med. — January 16, 2013. — Vol. 5(168). — doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004669.
24. Doria V. Magnetic resonance imaging of the preterm infant brain / V. Doria, T. Arichi, D. Edwards // Current. Pediatric. Reviews. — 2014. — Vol. 10. — P. 48-55.
25. Dubois J. Primary cortical folding in the human newborn: an early marker of later functional development / J. Dubois, M. Benders, C. Borradori-Tolsa et al. // Brain. — 2008. — Vol. 131. — P. 2028-2041.
26. Duerden E. Brain development in infants born preterm: looking beyond injury / E. Duerden, M. Taylor, S. Miller // Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. — 2013. — Vol. 20. — P. 65-74.
27. Dyet L. Natural history of brain lesions in extremely preterm infants studied with serial magnetic resonance imaging from birth and neurodevelopmental assessment / L. Dyet, N. Kennea, S. Counsell. et al. // Pediatrics. — 2006. — Vol. 118. — P. 536-548.
28. Ecury-Goossen G. The clinical presentation of preterm cerebellar haemorrhage / G. Ecury-Goossen, J. Dudink, M. Lequin et al. // Eur. J. Pediatr. — 2010. — Vol. 169. — P. 1249-1253.
29. Edwards A. Paediatric MRI under sedation: is it necessary? What is the evidence for the alternatives? / A. Edwards, O. Arthurs // Pediatr. Radiol. — 2011. — Vol. 41. — P. 1353-1364.
30. Engelhardt E. Regional impairments of cortical folding in premature infants / E. Engelhardt, T. Inder, D. Alexopoulos et al. // ANN. Neurol. — 2015. — Vol. 77. — P. 154-162.
31. van Haastert I. Decreasing incidence and severity of cerebral palsy in prematurely born children / I. van Haastert, F. Groenendaal, C. Uiterwaal et al. // J. Pediatr. — 2011. — Vol. 159(1). — P. 86-91.
32. Haney B. Magnetic resonance imaging studies without sedation in the neonatal intensive care unit: safe and efficient / B. Haney, D. Reavey, L. Atchison et al. // J. Perinat. Neonatal. Nurs. — 2010. — Vol. 24(3). — P. 256-266.
33. Hart A. Magnetic resonance imaging and developmental outcome following preterm birth: review of current evidence / A. Hart, E. Whitby, P. Griffiths et al. // Dev. Med. Child Neurol. — 2008. — Vol. 50. — P. 655-663.
34. Hart A. Neuro-developmental outcome at 18 months in premature infants with diffuse excessive high signal intensity on MR imaging of the brain / A. Hart, E. Whitby, S. Wilkinson et al. // Pediatr. Radiol. — 2011. — Vol. 41(10). — P. 1284-1292.
35. Harteman J. Atypical timing and presentation of periventricular haemorrhagic infarction in preterm infants: the role of thrombophilia / J. Harteman, F. Groenendaal, I.C. van Haastert et al. // Dev. Med. Child Neurol. — 2012. — Vol. 54(2). — P. 140-147.
36. Hillenbrand С. MR imaging of the newborn: a technical perspective / C. Hillenbrand, A. Reykowski // Magnetic resonance imaging clinics of North America. — 2012. — Vol. 20. — P. 63-79.
37. Hoon A. Pathogenesis, neuroimaging and management in children with cerebral palsy born preterm / A. Hoon, A. Fari // Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. — 2010. — Vol. 16(4). — P. 302-312.
38. Howson C. Born too soon: preterm birth matters / C. Howson, M. Kinney, L. McDougall et al. // Reprod. Health. — 2013. — Vol. 10, Suppl. 1. — S1.
39. Inder T. White matter injury in the premature infant: a comparison between serial cranial sonographic and MR findings at term / T. Inder, N. Anderson, C. Spencer et al. // Am. J. Neuroradiol. — 2003. — Vol. 24. — P. 805-809.
40. Intrapiromkul J. Accuracy of head ultrasound for the detection of intracranial hemorrhage in preterm neonates: comparison with brain MRI and susceptibility-weighted imaging / J. Intrapiromkul, F. Northington, T. Huisman et al. // J. Neuroradiol. — 2013. — Vol. 40(2). — P. 81-88.
41. Jary S. Impaired brain growth and neurodevelopment in preterm infants with posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation / S. Jary, A. De Carli, L. Ramenghi, A. Whitelaw et al. // Acta Paediatr. — 2012. — Vol. 101(7). — P. 743-748.
42. Jeon T. Neurodevelopmental jutcomes in preterm infants: comparison of infants with and without diffuse excessive high signal intensity on MR images at near-term-equivalent age / T. Jeon, J. Kim, S. Yoo et al. — Radiology. — 2012. — Vol. 263(2). — P. 518-526.
43. Kersbergen K. Different patterns of punctate white matter lesions in serially scanned preterm infants / K. Kersbergen, M. Ben–ders, F. Groenendaal et al. // PLoS One. — 2014. — Vol. 9(10). — e108904.
44. Kersbergen K. Corticospinal tract injury precedes thalamic volume reduction in preterm infants with cystic periventricular leukomalacia / K. Kersbergen, L. de Vries, F. Groenendaal et al. // J. Pediatr. — 2015. — Vol. 167(2). — P. 260-268.
45. Kidokoro H. A new MRI assessment tool to define brain abnormalities in very preterm infants at term / H. Kidokoro, J. Neil, T. Inder // Am. J. Neuroradiol. — 2013. — Vol. 34(11). — P. 2208-2214.
46. Kidokoro H. Brain injury and altered brain growth in preterm infants: predictors and prognosis / H. Kidokoro, P. Anderson, L. Doyle et al. // Pediatrics. — 2014. — Vol. 134(2). — P. e444-e453.
47. Kwon S. The role neuroimaging in predicting neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm neonates / S. Kwon, L. Vasung, L. Ment et al. // Clin. Perinatol. — 2014. — Vol. 41. — P. 257-283.
48. Larroque B. Neurodevelopmental disabilities and special care of 5-year-old children born before 33 weeks of gestation (the EPIPAGE study): a longitudinal cohort study / B. Larroque, P. Ancel, S. Marret // Lancet. — 2008. — Vol. 371(965). — P. 813-820.
49. Leijser L.M. Is sequential cranial ultrasound reliable for detection of white matter injury in very preterm infants? / L.M. Leijser, F.T. Bruine, J. Grond et al. // Neuroradiology. — 2010. — Vol. 52. — P. 397-406.
50. Limperopoulos C. Injury to the premature cerebellum: outcome is related to remote cortical development / C. Limperopoulos, G. Chilingaryan, N. Sullivan et al. // Cerebral. Cortex. — 2014. — Vol. 24. — P. 728-736.
51. Liu L. Global, regional and national causes of child morta-lity: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000 / L. Liu, H. Johnson, S. Cousens et al. // Lancet. — 2012. — Vol. 379. — P. 2151-2161.
52. Lodygensky G. Neuroimaging of cortical development and brain connectivity in human newborns and animal models / G. Lodygensky, L. Vasung, S. Sizonenko et al. // J. Anat. — 2010. — Vol. 217. — P. 418-428.
53. Marlow N. Neurologic and developmental disability at six years of age after extremely preterm birth / N. Marlow, D. Wolke, M.A. Bracewell et al. // N. Engl. J. Med. — 2005. — Vol. 352. — P. 9-19.
54. Marret S. Brain injury in very preterm children and neurosensory and cognitive disabilities during childhood: the EPIPAGE cohort study / S. Marret, L. Marchand-Martin, J. Picaud et al. // PLoS One. — 2013. — Vol. 8(5). — e62683.
55. Mathur A. Understanding brain injury and neurodevelopmental disabilities in the preterm infant: the evolving role of advanced MRI / A. Mathur, J.J. Neil, T. Inder // Semin. Perinatol. — 2010. — Vol. 34(1). — P. 57-66.
56. Maunu J. Ventricular dilatation in relation to outcome at 2 years of age in very preterm infants: a prospective Finnish cohort study / J. Maunu, L. Lentonen, H. Lapinleimu et al. // Dev. Med. Child Neurol. — 2011. — Vol. 53. — P. 48-54.
57. Ment L. Imaging biomarkers of outcome in the developing preterm brain / L. Ment, D. Hirtz, P. Huppi // Lancet. — 2009. — Vol. 8(11). — P. 1045-1055.
58. Miller S. Early brain injury in premature newborns detected with magnetic resonance imaging is associated with adverse early neurodevelopmental outcome / S. Miller, D. Ferriero, C. Leonard et al. // J. Pediatr. — 2005. — Vol. 147. — P. 609-616.
59. Moeskops P. Development of cortical morphology evaluated with longitudinal MR brain images of preterm infants / P. Moeskops, M. Benders, K. Kersbergen et al. // PLoS One. — 2015. — Vol. 10. — e0131552.
60. Moore T. Neurological and developmental outcome in extremely preterm children born in England in 1995 and 2006: the EPICure studies / T. Moore, E.M. Hennessy, J. Myles et al. // BMJ. — 2012. — Vol. 345. — e7961.
61. Nagy Z. Effects of preterm birth on cortical thickness measured in adolescence / Z. Nagy, H. Lagercrantz, C. Hutton // Cerebral Cortex. — 2011. — Vol. 21. — P. 300-306.
62. Neubauer V. Feasibility of cerebral MRI in non-sedated preterm-born infants at term-equivalent age: report of a single centre / V. Neubauer, E. Griesmaier, K. Baumgartner et al. // Acta Paediatr. — 2011. — Vol. 100. — P. 1544-1547.
63. Niwa T. Punctate white matter lesions in infants: new insights using susceptibility-weighted imaging / T. Niwa, L. Vries, M. Benders et al. // Neuroradiology. — 2011. — Vol. 53. — P. 669-679.
64. Nosarti C. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm birth: from childhood to adult life / C. Nosarti, R. Murray, M. Hack. — Cambridge: University Press, 2010. — C. 39-53.
65. Nosarti C. Neonatal ultrasound results following very preterm birth predict adolescent behavioral and cognitive outcome / C. Nosarti, M. Walshe, T.M. Rushe et al. // Developmental Neuropsycho–logy. — 2011. — Vol. 36. — P. 118-135.
66. Nosarti C. Preterm birth and structural brain alterations in early adulthood / C. Nosarti, K. Nam, M. Walshe et al. // NeuroIma–ge: Clinical. — 2014. — Vol. 6. — P. 180-191.
67. Omizzolo C. Neonatal brain abnormalities and memory and learning outcomes at 7 years in children born very preterm / C. Omizzolo, S. Scratch, R. Stargatt et al. // Memory. — 2014. — Vol. 22(6). — P. 605-616.
68. Panigrahy A. Neuroimaging biomarkers of preterm brain injury: toward developing the preterm connectome / A. Panigrahy, J.L. Wisnowski, A. Furtado et al. // Pediatr. Radiol. — 2012. — Vol. 42(01). — S33-S61.
69. Papile L. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm / L. Papile, J. Burstein, R. Burstein et al. // J. Pediatr. — 1978. — Vol. 92. — P. 529-534.
70. Parikh N. Automatically quantified diffuse excessive high signal intensity on MRI predicts cognitive development in preterm infants / N. Parikh, L. He, E. Bonfante-Mejia // Pediatr. Neurol. — 2013. — Vol. 49(6). — P. 424-430.
71. Parodi A. Accuracy of ultrasound in assessing cerebellar haemorrhages in very low birthweight babies / A. Parodi, A. Rossi, M. Severino et al. // Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. — 2015. — Vol. 100(4). — F289-292.
72. Rathbone R. Perinatal cortical growth and childhood neurocognitive abilities / R. Rathbone, S. Counsell, O. Kapellou et al. // Neurology. — 2011. — Vol. 77. — P. 1510-1517.
73. Plaisier A. Serial cranial ultrasonography or early MRI for detecting preterm brain injury? / A. Plaisier, M. Raets, G. Ecury-Goossen et al. // Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. — 2015. — Vol. 100(4). — F293-300.
74. Roze E. Neonatal DTI early after birth predicts motor outcome in preterm infants with periventricular hemorrhagic infarction / E. Roze, M. Benders, K. Kersbergen et al. // Pediatr. Res. — 2015. — Vol. 78(3). — P. 298-303.
75. Soltirovska Salamon A. Neuroimaging and neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm infants with a periventricular haemorrhagic infarction located in the temporal or frontal lobe / A. Sol–tirovska Salamon, F. Groenendaal, I.C. van Haastert et al. // Dev. Med. Child Neurol. — 2014. — Vol. 56(6). — P. 547-555.
76. Serenius F. Neurodevelopmental outcome in extremely preterm infants at 2.5 years after active perinatal care in Sweden / F. Serenius, K. Källén, M. Blennow et al. // JAMA. — 2013. — Vol. 309(17). — P. 1810-1820.
77. Smyser С. MRI of the brain at term equivalent age in extremely premature neonates — to scan or not to scan? / C. Smyser, H. Kidokoro, T. Inder // J. Paediatr. Child Health. — 2012. — Vol. 48(9). — P. 794-800.
78. Smyser T. Cortical gray and adjacent white matter demonstrate synchronous maturation in very preterm infants / T. Smyser, C. Smyser, C. Rogers et al. // Cereb. Cortex. — Jul 24, 2015. — pii: bhv164.
79. Steggerda S. Cerebellar injury in preterm infants: incidence and findings on US and MR images / S. Steggerda. L. Leijser, F. Wiggers-de Bruїne et al. // Radiology. — 2009. — Vol. 252. — P. 190-199.
80. Steggerda S. Small cerebellar hemorrhage in preterminfants: perinatal and postnatal factors and outcome / S. Steggerda, F. de Bruїne, A. van den Berg-Huysmans // Cerebellum. — 2013. — Vol. 12(6). — P. 794-801.
81. Stoll B. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network / B. Stoll, N. Hansen, E. Bell et al. // Pediatrics. — 2010. — Vol. 126. — P. 443-456.
82. Tao J. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging techniques in the preterm brain: methods and applications / J. Tao, J. Neil // Current Pediatric Reviews. — 2014. — Vol. 10. — P. 56-64.
83. Tusor N. Brain development in preterm infants assessed using advanced MRI techniques / N. Tusor, T. Arichi, S. Counsell et al. // Clin. Perinatol. — 2014. — Vol. 41(1). — P. 25-45.
84. Volpe J.J. Neurology of the Newborn / J.J. Volpe. — Philadelphia: Saunders, 2008. — P. 517-588.
85. Volpe J. Cerebellum of the premature infant: rapidly develo–ping, vulnerable, clinically important / J. Volpe // J. Child Neurol. — 2009. — Vol. 24. — P. 1085-1104.
86. de Vries L. Myth: cerebral palsy cannot be predicted by neonatal brain imaging / L.Vries, I. Haastert, M. Benders, F. Groenendaal // Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. — 2011. — Vol. 16(5). — P. 279-287.
87. de Vries L. Progress in neonatal neurology with a focus on neuroimaging in the preterm infant / L. Vries, M. Benders, F. Groenendaal // Neuropediatrics. — 2015. — Vol. 46. — P. 234-241.
88. Wezel-Meijler G. Cranial ultrasonography in neonates: role and limitations / G. Wezel-Meijler, S. Steggerda, L.M. Leijser // Semin. Perinatol. — 2010. — Vol. 34. — P. 28-38.
89. Wezel-Meijler G. Cranial ultrasound — optimizing utility in the NICU / G. Wezel-Meijler, L.S. Vries // Current. Pediatric. Reviews. — 2014. — Vol. 10(1). — P. 16-27.
90. Woodward L. Neonatal MRI to predict neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants / L. Woodward, P. Anderson, N. Austin et al. // N. Engl. J. Med. — 2006. — Vol. 355. — P. 685-694.
91. Zimmerman R. Neuroimaging: clinical and physical principles / R. Zimmerman, W. Gibby, R. Carmody. — New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. — C. 491-584.

/45.jpg)
/47_2.jpg)
/48.jpg)