Журнал «Травма» Том 24, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Інтегральна оцінка якості ходьби хворих на гонартроз до та після ендопротезування
Авторы: Обейдат Халед Джамал Салех (1), Карпінська О.Д. (2)
(1) — Вінницький національний медичний університет ім. М.І. Пирогова, м. Вінниця, Україна
(2) — ДУ «Інститут патології хребта та суглобів ім. проф. М.І. Ситенка НАМН України», м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
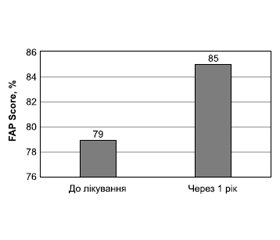
Актуальність. Остеоартроз колінного суглоба супроводжується не тільки болем, але й значним порушенням патернів стояння та ходьби. Часто ускладнюється контрактурою та вираженою кульгавістю. Це впливає не тільки на стан хворого суглоба, але й на протилежний суглоб. Для оцінки якості ходьби використовують інтегральний показник якості ходьби — Functional Ambulation Perfomance Score (FAPS, FAP Score — функціональна здатність пересування). FAPS базується на основних параметрах ходьби, які отримані при дослідженні, і являє собою кількісну оцінку ходьби пацієнтів. Мета: оцінити якість ходьби за показником FAPS у пацієнтів з гонартрозом до та після ендопротезування колінного суглоба. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 23 пацієнти з гонартрозом. Вік хворих становив у середньому 61,5 ± 9,2 року, від 36 до 73 років. Обстеження проводили після одностороннього ендопротезування. У всіх хворих ендопротезування було первинним. Обстеження проводили за допомогою системи GAITRite. Інтегральний показник (FAP) оцінюється як добрий при 85–95 %, задовільний — 70–84 % та незадовільний — нижче ніж 69 %. Знижує оцінку FAP наявність додаткових засобів опори. Результати. Серед хворих, які пройшли обстеження до ендопротезування, 10 (43 %) пацієнтів користувалися додатковою опорою (милицями або палицею), 13 (56 %) хворих не користувалися додатковою опорою, хоча мали виражену кульгавість. Означені особливості ходьби враховувалися при обчисленні FAP. Через 1 рік після ендопротезування палицею продовжували користуватися 2 (8,6 %) пацієнти, 3 (13, %) — користувалися додатковою опорою при тривалій ходьбі. Такі пацієнти були старші від 60 років. Визначено, що до лікування FAP хворих мав великий діапазон значень — від 47 %, що оцінюється як незадовільний стан, до 99 % — добрий результат. Це обумовлено станом хворих, які звернулися для лікування, — ранній період захворювання, коли зміни ходьби ще не набули стійких патологічних ознак, чи хворі з тривалим перебігом, коли вже були сформовані хибні звички пересування. Але, за даними аналізу, у хворих у середньому підвищився рівень FAP. Треба відмітити, що у хворих, FAP яких був більше ніж 95 %, через рік спостерігалося його зменшення на декілька відсотків, але не нижче ніж 94 %, а у хворих, FAP яких оцінювався як незадовільний, його рівень підвищився до 70 % (задовільний). Хворі похилого віку продовжували користуватися додатковими засобами опори, що також знижувало оцінку FAP, хоча рентгенологічний результат ендопротезування оцінювався як добрий. Зменшення больового синдрому та відновлення опірності кінцівки збільшує показник функціональності ходьби. Однак треба враховувати, що остеоартроз є системним захворюванням і розвивається частіше на обох колінних суглобах, часто в дегенеративний процес залучаються інші структури скелета. Тому у хворих похилого віку FAP після ендопротезування сягає задовільних значень. Треба відмітити, що ми розглядали хворих після ендопротезування на одному колінному суглобі, а це не завжди дає одразу очікуваний добрий результат. Висновки. Інструментальні методи дослідження ходьби хворих дозволяють визначити ступінь порушення динаміки. Ендопротезування колінного суглоба усуває больовий синдром і відновлює опірність кінцівки, що сприяє поліпшенню ходьби. Цей метод оцінки ходьби дає можливість визначити ступінь відновлення хворих та скоригувати подальші методи корекції ходьби чи план подальшого лікування.
Background. Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is accompanied not only by pain, but also by a significant disturbance of standing and gait patterns. It is often complicated by contracture and severe lameness. This influences not only the state of the affected joint, but also the opposite one. To evaluate the quality of gait, an integral indicator is used — Functional Ambulation Performance Score (FAPS). The FAPS is based on the main parameters of gait and is a quantitative assessment of the gait of patients obtained during the study. The purpose was to evaluate the quality of gait according to the FAPS in patients with gonarthrosis before and after knee arthroplasty. Materials and methods. Twenty-three patients with gonarthrosis were examined. Their age was on average 61.5 ± 9.2 years, from 36 to 73 years. The examination was performed after unilateral arthroplasty. Arthroplasty was primary in all patients. The examination was carried out using the GAITRite system. The integral indicator (FAP) is evaluated as good at 85–95 %, satisfactory at 70–84 % and unsatisfactory at below 69 %. The use of additional means of support reduces the FAP. Results. Among patients who were examined before arthroplasty, 10 (43 %) people used additional support (crutches or cane), 13 (56 %) did not use it, although they had pronounced lameness. The specified features of gait were taken into account when calculating the FAP. One year after arthroplasty, 2 (8.6 %) patients continued to use a cane, 3 (13 %) used additional support for long walks. Such patients were older than 60 years. It was found that before the treatment, the FAP had a wide range — from 47 %, which is considered an unsatisfactory condition, to 99 % — a good result. This is due to the state of the patients who sought treatment — it was the early period of the disease, when the changes in gait have not yet acquired persistent pathological signs, or patients had a long disease course, when the wrong habits of movement have already been formed. But according to the analysis, the average level of FAP increased. It should be noted that in patients whose FAP was more than 95 %, it decreased by few percents in a year, but not below 94 %, and in people whose FAP was assessed as unsatisfactory, its level increased to 70 % (satisfactory). Elderly patients continued to use additional means of support, which also reduced the FAP, although the radiological result of arthroplasty was good. Reducing the pain syndrome and restoring the support ability of the limb increases the indicator of the functionality of gait. However, it should be taken into account that osteoarthritis is a systemic disease, develops more often in both knee joints, and other skeletal structures are often involved in the degenerative process. Therefore, the FAP of elderly patients after arthroplasty reaches satisfactory values. It should be noted that we examined patients after arthroplasty on one knee joint, and this does not always immediately give the expected good result. Conclusions. Instrumental methods for studying patients’ gait make it possible to determine the degree of dynamic disturbance. Knee arthroplasty eliminates the pain syndrome and restores the support ability of the limb, which contributes to the improvement of gait. This method of gait assessment allows determining the degree of patients’ recovery and adjust further methods of gait correction or a plan of treatment.
FAP Score; колінний суглоб; гонартроз; ходьба
Functional Ambulation Performance Score; knee joint; gonarthrosis; gait