Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №8, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Сучасні тенденції грудного вигодовування дітей
Авторы: A. Kachurenko, L. Levadna, A. Horobets, Yu. Proshchenko, Ya. Kalinichenko
Bogomolets National Medical University, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
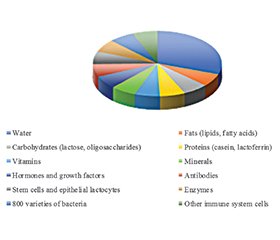
Грудне вигодовування є критично важливим аспектом догляду за немовлям, що забезпечує численні переваги як для немовлят, так і для матерів. Соціокультурні зміни ХХІ століття вимагають оптимізації цієї практики й дослідження фізіологічних етапів секреції молока, включаючи гормональну регуляцію лактації та фактори, які впливають на секрецію грудей, що має вирішальне значення для підтримки грудного вигодовування та покращення загального самопочуття немовлят і матерів. Ця робота має на меті вивчити сучасні погляди на підтримку грудного вигодовування шляхом всебічного огляду існуючої літератури з особливим акцентом на дослідженнях фізіологічних етапів секреції молока під час вагітності та годування груддю. Використовувалися бібліографічний, аналітичний методи та нормативний пошук. Цей огляд сприяє поглибленню знань і розумінню грудного вигодовування, підкреслюючи його важливість для догляду за новонародженим та благополуччя матері. Матеріал охоплює широкий спектр факторів, що впливають на лактацію як фізіологічний процес і грудне вигодовування як соціальну практику. Отримані дані підкреслюють фізіологічну основу процесу лактації: ключову роль пролактину та окситоцину в ініціюванні та підтримці секреції молока, внутрішні (гормональний дисбаланс, анатомія грудей та хірургічне втручання), а також зовнішні фактори, такі як соматичний стан матері, включаючи гестаційний період, діабет і синдром полікістозних яєчників. Проаналізовано позитивні сторони грудного вигодовування як для дитини, так і для матері. Розглянуто різноманітні позитивні наслідки цієї практики для дитини, зокрема сприятливий баланс поживних речовин у молоці матері, формування пасивного імунітету та підтримання здорової мікробіоти кишечника. Особливу увагу приділено мінливим поглядам на вигодовування немовлят у світлі соціальних та економічних змін на початку ХХІ століття, включаючи зростаючу роль штучних сумішей і виклики природного вигодовування на робочому місці. Практичні наслідки: це забезпечує основу для розробки науково обґрунтованих втручань щодо покращення досвіду грудного вигодовування та благополуччя як немовлят, так і матерів, одночасно інформуючи медичних працівників, політиків та групи підтримки.
Breastfeeding is a critical aspect of infant care that provides numerous benefits for both infants and mothers. The socio-cultural changes of the 21st century require optimisation of this practice and research into the physiological stages of milk secretion, including the hormonal regulation of lactation and factors that influence breast secretion, which is crucial for supporting breastfeeding and improving the overall well-being of infants and mothers. The purpose of the work was to investigate current views on breastfeeding support through a comprehensive review of the existing literature, with a particular focus on studies on the physiological stages of milk secretion during pregnancy and breastfeeding. We used bibliographic, analytical and regulatory search methods. The review contributes to the deepening of knowledge and understanding of breastfeeding, emphasising its importance for newborn care and maternal well-being. The material covers a wide range of factors that influence lactation as a physiological process and breastfeeding as a social practice. The findings highlight the physiological basis of the lactation process: the key role of prolactin and oxytocin in initiating and maintaining milk secretion, internal (hormonal imbalances, breast anatomy and surgery), and external factors such as the mother’s somatic condition, including gestational diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. The positive aspects of breastfeeding for both the child and the mother are analysed. The various positive effects of this practice on the child are considered, including the most favourable balance of nutrients in the mother’s milk, the formation of passive immunity and the maintenance of a healthy intestinal microbiota. Particular attention is paid to the changing views on infant feeding in light of social and economic changes in the early 21st century, including the growing role of artificial formula and the challenges of natural feeding in the workplace. Practical implications: it provides a basis for developing evidence-based interventions to improve the breastfeeding experience and well-being of both infants and mothers while informing healthcare professionals, policymakers, and support groups.
лактація; гормональний контроль; фізіологічні стадії; імунітет дитини; фактори впливу
lactation; hormonal control; physiological stages; child’s immunity; factors of influence
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Bila V.V., Zahorodnia O.S., Baryshnikova VV. Breast milk bank of Kyiv perinatal center — Experience in 2022. Reprod. Health Woman. 2023. 2(65). 10-13.
- Marushko R.V., Dudina О.О., Marushko T.L. Analysis of the health status of children of the first year of life. Mod. Pediatr. Ukr. 2020. 5(109). 24-32.
- Starets O.O., Khimenko T.M., Kotova N.V., Ismayilova S.I., Kanarova O.V. Risk factors and short-term consequences of the absence or early cessation of breastfeeding in infants born preterm. Ukr. J. Perinatol. Pediatr. 2023. 1(93). 57-63.
- Abaturov O.E., Tovarnytska A.O. Prognostic significance of the breast milk microRNA impact on the immune response of a newborn with intrauterine growth retardation. Mod. Pediatr. Ukr. 2021. 1(113). 53-61.
- Grundy S.J., Hardin A., Kuller J.A., Dotters-Katz S. Breastfee–ding: The basics, the history, and barriers in the modern day. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2022. 77(7). 423-432.
- Feldman-Winter L., Kellams A., Peter-Wohl S., Taylor J.S., Lee K.G. et al. Evidence-based updates on the first week of exclusive breastfeeding among infants ≥ 35 weeks. Pediatr. 2020. 145(4). e20183696.
- Cummins L., Meedya S., Wilson V. Factors that positively influence in-hospital exclusive breastfeeding among women with gestational diabetes: An integrative review. Women Birth. 2022. 35(1). 3-10.
- Koksal I., Acikgoz A., Cakirli M. The effect of a father’s support on breastfeeding: A systematic review. Breastfeed. Med. 2022. 17(9). 711-722.
- Russell M.D., Dey M., Flint J., Davie P., Allen A. et al., BSR Standards, Audit and Guidelines Working Group. British Society for Rheumatology guideline on prescribing drugs in pregnancy and breastfee–ding: Immunomodulatory anti-rheumatic drugs and corticosteroids. Rheumatol. 2023. 62(4). e48-e88.
- Dawod B., Marshall J.S., Azad M.B. Breastfeeding and the developmental origins of mucosal immunity: How human milk shapes the innate and adaptive mucosal immune systems. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2021. 37(6). 547-556.
- Eidelman A.I. Telemedicine and breastfeeding: The time has come. Breastfeed. Med. 2021. 16(4). 273-274.
- Sayres S., Visentin L. Breastfeeding: Uncovering barriers and offering solutions. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018. 30(4). 591-596.
- Vandenplas Y. Breastfeeding and its risk factors. J. Pediatr. 2022. 98(3). 219-220.
- Qiu R., Zhong Y., Hu M., Wu B. Breastfeeding and reduced risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022. 8500910.
- Westerfield K.L., Koenig K., Oh R. Breastfeeding: Common questions and answers. Am. Fam. Physician. 2018. 98(6). 368-376.
- Rollins N.C., Bhandari N., Hajeebhoy N., Horton S., Lutter C.K. et al., Lancet Breastfeeding Series Group. Why invest, and what it will take to improve breastfeeding practices? Lancet. 2016. 387(10017). 491-504.
- Sattari M., Serwint J.R., Levine D.M. Maternal implications of breastfeeding: A review for the internist. Am. J. Med. 2019. 132(8). 912-920.
- Carr L.E., Virmani M.D., Rosa F., Munblit D., Matazel K.S. et al. Role of human milk bioactives on infants’ gut and immune health. Front. Immunol. 2021. 12. 604080.
- Magro I., Nurimba M., Doherty J.K. Headache in pregnancy. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2022. 55(3). 681-696.
- Omranipour R., Vasigh M. Mastitis, breast abscess, and granulomatous mastitis. In: Dis Breast Pregnancy and Lactation. 2020. 53-61. Cham: Springer.
- Gianni M.L., Bettinelli M.E., Manfra P., Sorrentino G., Bezze E. et al. Breastfeeding difficulties and risk for early breastfeeding cessation. Nutrients. 2019. 11(10). 2266.
- Levene I., O’Brien F. Fifteen-minute consultation: Breastfeeding in the first 2 weeks of life — A hospital perspective. Arch. Dis. Child Educ. Pract. 2019. 104(1). 20-26.
- Van Dellen S.A., Wisse B., Mobach M.P., Dijkstra A. The effect of a breastfeeding support programme on breastfeeding duration and exclusivity: A quasi-experiment. BMC Public Health. 2019. 19. 993.
- Fisher J. Recommendations against breastfeeding require consultation with women for effective implementation. Lancet Glob. Health. 2023. 11(5). E648-E649.
- Patel S., Patel Sh. The effectiveness of lactation consultants and lactation counselors on breastfeeding outcomes. J. Hum. Lact. 2016. 32(3). 530-541.
- You H., Lei A., Xiang J., Wang Y., Luo B., Hu J. Effects of breastfeeding education based on the self-efficacy theory on women with gestational diabetes mellitus: A CONSORT-compliant randomized controlled trial. Med. 2020. 99(16). e19643.
- Svyatova G.S., Mirzakhmetova D.D., Berezina G.M., Murtazaliyeva A.V. Genetic Factors of Idiopathic Recurrent Miscarriage in Kazakh Population. J. Reproduct. Infertil. 2022. 23(1). 39-45.
- Svyatova G., Mirzakhmetova D., Berezina G., Murtazaliyeva A. Immunogenetic aspects of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage in the Kazakh population. J. Med. Life 2021. 14(5). 676-682.
- Aktaeva L.M., Mirzakhmetova D.D., Padaiga Z. Extragenital pathologies of pregnant women in the southern regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan. System Rev. Pharm. 2020. 11(4). 405-412.
- Yessentayeva S.Y., Orakbay L.Z., Adilhanova A., Yessimov N. Approaches to the use of stem cells in regenerative medicine. Analyt. Biochem. 2022. 645. 114608.
- Zaychenko G., Stryga O., Sinitsyna O., Doroshenko A., Sulaie–va O., Falalyeyeva T., Kobyliak N. Resveratrol Effects on the Reproductive System in Ovariectomized Rats: Deciphering Possible Mechanisms. Molec. 2022. 27(15). 4916.
- Ciechanowicz P., Lewandowski K., Szymańska E., Kaniewska M., Rydzewska G.M., Walecka I. Skin and gastrointestinal symptoms in COVID-19. Przeglad Gastroenterol. 2020. 15(4). 301-308.
- Hajiyeva N.N. Clinical presentations of pain syndrome depending on the grade of CNS lesions at newborns. Azerb. Med. J. 2008. (3). 50-52.
- Pylypchynets I. Optimal scheme for stimulating photofission of shielded nuclear materials on the Microtron M-30: a combination of theoretical and experimental studies. Sci. Her. Uzhhor. Univer. Ser. Phys. 2022. 52. 16-26.
- Lukianenko N., Kens O., Nurgaliyeva Z., Toguzbayeva D., Sakhipov M. Finding a molecular genetic marker for the incidence of recurrent episodes of acute obstructive bronchitis in children. J. Med. Life 2021. 14(5). 695-699.
- Lukyanenko N., Lenha E., Spaska A., Klets T., Shevchenko T. Tactics for treating young children with pyelonephritis and vesicoureteral reflux associated with impaired fibrillogenesis. Molec. Cell. Biochem. 2023. 478(3). 531-538.
- Stepanov V.A., Bocharova A.V., Saduakassova K.Z., Marusin A.V., Koneva L.A., Vagaitseva K.V., Svyatova G.S. Replicative study of susceptibility to childhood-onset schizophrenia in Kazakhs. Genet. 2015. 51(2). 227-235.
- Rhodes E.C., Damio G., LaPlant H.W., Trymbulak W., Crummett C., Surprenant R., Pérez-Escamilla R. Promoting equity in breastfeeding through peer counseling: The US breastfeeding heritage and pride program. Int. J. Equity Health. 2021. 20. 128.
- Dutheil F., Méchin G., Vorilhon P., Benson A.C., Bottet A. et al. Breastfeeding after returning to work: A systematic review and meta-ana–lysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021. 18(16). 8631.
- Zharmakhanova G., Syrlybayeva L., Nurbaulina E., Baika–damova L., Eshtayeva G. Inborn errors of fatty acid metabolism (review). Georg. Med. News 2020. (303). 161-167.
- Zharmakhanova G., Syrlybayeva L., Kononets V., Nurbaulina E., Baikadamova L. Molecular-genetic aspects of methylmalonic aciduria development (review). Georg. Med. News 2021 (313). 118-124.