Международный неврологический журнал Том 20, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Особливості структурних та функціональних змін органів черевної порожнини при хворобі Вільсона
Авторы: I.K. Voloshyn-Haponov (1, 2), I.I. Chernenko (1), N.P. Voloshyna (2)
(1) - V.N. Karazin Kharkiv National University, Kharkiv, Ukraine
(2) - State Institution “Institute of Neurology, Psychiatry and Narcology of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine”, Kharkiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Неврология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
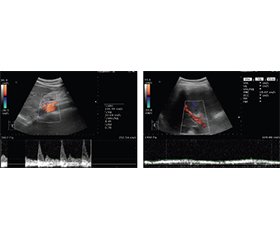
У статті наведено результати ультразвукової діагностики 76 осіб із неврологічними формами гепатоцеребральної дистрофії, або хвороби Вільсона (ХВ), яких обстежували та лікували в клініці Інституту неврології, психіатрії та наркології НАМН України. За даними ультразвукової діагностики, у всіх пацієнтів спостерігалися патологічні зміни в печінці. У 58 % випадків вони відповідали хронічному гепатиту, у 42 % — цирозу печінки. Ознаки портальної гіпертензії мали 32 % хворих. Допплерометрія показала, що фонова печінкова гемодинаміка в пацієнтів із неврологічними формами гепатоцеребральної дистрофії була в межах норми, але у 82 % із них спостерігається порушення реципрокної авторегуляції мікроциркуляції органа. Це свідчить про зменшення компенсаторно-адаптивних можливостей печінки. Таке положення підтверджується тим, що 70 % цих хворих мають зниження вазоактивної функції ендотелію. Загалом по групі показник становив лише 8,12 % при нормі 10 % і більше. Незважаючи на молодий вік наших пацієнтів (у середньому 29,7 року), лише в 30 % вазоактивна реакція була нормальною. Це були особи віком до 25 років із хронічним гепатитом. Хворі на цироз печінки мали вірогідно вищий ступінь ендотеліальної дисфункції порівняно з особами з хронічним гепатитом. За даними ультразвукової еластографії, у переважної більшості обстежених пацієнтів із ХВ (88 %) спостерігалося підвищення жорсткості паренхіми печінки. У середньому по групі вона становила 10,62 кПа з діапазоном від 4,74 до 20,69 кПа (норма 0,4–6,0 кПа). Таким чином, пацієнти з неврологічними формами ХВ, які спостерігаються в невропатолога, повинні проходити ультразвукове дослідження органів черевної порожнини перед кожним курсом лікування, але не рідше 1–2 разів на рік.
The paper presents the results of the ultrasound diagnosis of 76 patients with neurological forms of hepatocerebral dystrophy, or Wilson’s disease (WD), who were examined and treated at the clinic of the Institute of Neurology, Psychiatry and Narcology of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine. According to ultrasound diagnosis, all patients had pathological changes in the liver. In 58 % of patients, these changes corresponded to chronic hepatitis, in 42 % — to liver cirrhosis. 32 % of patients had evidence of portal hypertension. A Doppler test showed that background hepatic hemodynamics in patients with neurological forms of hepatocerebral dystrophy was within normal limits, but 82 % of patients had an impaired reciprocal autoregulation of liver microcirculation. It indicates a decrease in the compensatory and adaptive capabilities of the liver. This position is confirmed by the fact that 70 % of such patients have a decrease in the vasoactive function of the endothelium. In general, the indicator for the group was only 8.12 %, with a norm of 10 % or more. Despite the young average age of our patients (29.7 years), only 30 % of them had a normal vasoactive reaction. These were patients under the age of 25 with chronic hepatitis. The degree of endothelial dysfunction was significantly higher in patients with liver cirrhosis compared to those with chronic hepatitis. According to ultrasound elastography, most examined patients with WD (88 %) had increased stiffness of the liver parenchyma. On average, it was 10.62 kPa with a range from 4.74 to 20.69 kPa (norm 0.4–6.0 kPa). Thus, patients with neurological forms of WD who are observed by a neuropathologist should undergo an abdominal ultrasound before each course of treatment, but at least 1–2 times a year.
хвороба Вільсона; печінка; ультразвукова діагностика; допплерографічне дослідження; гемодинамічні зміни
Wilson’s disease; liver; ultrasound diagnosis; Doppler examination; haemodynamic changes