Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 19, №6, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Значення дисфункції шкірного бар’єра при атопічному дерматиті та можливості її корекції
Авторы: Няньковська О.С.1, 2, Няньковський С.Л.1, 2, Городиловська М.І.1, Камуть Н.В.1
1Львівський національний медичний університет імені Данила Галицького, м. Львів, Україна
2Інститут наук про здоров'я, Медичний коледж Жешувського університету, м. Жешув, Польща
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
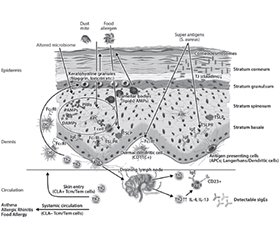
Атопічний дерматит (АД) — це хронічний рецидивуючий екзематозний дерматоз, який уражає до 20 % дітей та 10 % дорослих. Патофізіологія передбачає взаємодію між дисфункціональним шкірним бар’єром та спотвореною вродженою й набутою імунною реакцією 2-го типу з невідповідною активацією клітин Th2 і вроджених лімфоїдних клітин 2-го типу. Порушення шкірного бар’єра при AД включає аномалії ороговілої оболонки, ліпідних ламелей, щільних з’єднань, мікробіому, що також може бути і на шкірі без уражень AД, таким чином, припускається, що дефекти епідермального бар’єра передують розвитку клінічних проявів AД і, зрештою, інших пов’язаних алергічних захворювань. Численні фактори, включно з імунною дисрегуляцією, дефектами диференціації термінального епітелію, як-от відсутність філагрину, дефіцитом антимікробних пептидів, зміненим складом міжклітинних ліпідів рогового шару та зміненим мікробіомом шкіри, спричиняють дефекти шкірного бар’єра. Пом’якшувальні засоби відіграють ключову роль у профілактиці, лікуванні й підтриманні ремісії АД. Крем Бепантен® Сенсідерм має спеціальну формулу без гормонів, яка полегшує симптоми АД легкого та помірного ступенів тяжкості шляхом відновлення пошкодженого шкірного бар’єра.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic relapsing eczematous dermatosis that affects up to 20 % of children and 10 % of adults. Pathophysiology involves an interplay between a dysfunctional skin barrier and skewed type 2 innate and adaptive immune responses, with an inappropriate activation of Th2 cells and type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Impaired skin barrier in AD includes abnormalities in the cornified envelope, lipid lamellae, tight junctions and cutaneous microbiome, which are also present in non-lesional AD skin, thus suggesting that epidermal barrier defects precede the development of the clinical AD manifestations, and other related allergic diseases. Multiple factors, including immune dysregulation, defects in terminal epithelial differentiation such as lack of filaggrin, deficiency of antimicrobial peptides, altered composition of stratum corneum intercellular lipids, and altered skin microbiome, cause skin barrier defects. Emollients play a key role in the prevention, treatment and maintenance of AD remission. Bepanthen® Sensiderm cream has a special hormone-free formula that relieves the symptoms of mild to moderate AD by restoring the damaged skin barrier.
шкірний бар’єр; філагрин; корнеодесмосоми; ліпідні ламелі; атопічний дерматит; емолієнти; крем Бепантен® Сенсідерм
skin barrier; filaggrin; corneodesmosomes; lipid lamellae; atopic dermatitis; emollients; Bepanthen® Sensiderm cream
Шкірний бар’єр при AД
/44.jpg)
Роговий шар при AД
/45.jpg)
/46.jpg)
/47.jpg)
Біологічний бар’єр та Staphylococcus aureus при AД
/48.jpg)
- Gomes T, Calado R, Gonçalo M. Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of the Portuguese Society of Dermatology and Venereology. 2021;79:207-216. 10.29021/spdv.79.3.1405.
- Laughter MR, Maymone MB, Mashayekhi S, Arents BW, Karimkhani C, Langan SM, et al. The global burden of atopic dermatitis: lessons from the GBD Study — 1990 to 2017. Br J Dermatol. 2020;184:304-9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19580.
- Elmose C, Thomsen SF. Twin Studies of Atopic Dermatitis: Interpretations and Applications in the Filaggrin Era. J Allergy. 2015;2015:1-7. doi: 10.1155/2015/902359.
- Langan SM, Irvine AD, Weidinger S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2020;396:345-60. doi: 10.1016/ S0140-6736(20)31286-1.
- Kim J, Kim BE, Leung DY. Pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis: Clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019;40:84-92. doi: 10.2500/aap.2019.40.4202.
- Bin L, Leung DY. Genetic and epigenetic studies of atopic dermatitis. Allergy, Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016;12:52. doi: 10.1186/s13223-016-0158-5
- Cabanillas B, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and filaggrin. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016;42:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.05.002.
- Smieszek SP, Welsh S, Xiao C, Wang J, Polymeropoulos C, Birznieks G, et al. Correlation of age-of-onset of Atopic Dermatitis with Filaggrin loss-of-function variant status. Sci Rep. 2020;10:2721. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59627-7.
- De Benedetto A, Kubo A, Beck LA. Skin barrier disruption: a requirement for allergen sensitization? J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:949-63. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.435.
- Fujii M. Current understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms of atopic dermatitis: interactions among skin barrier dysfunction, immune abnormalities and pruritus. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43:12-9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00088.
- Moyle M, Cevikbas F, Harden JL, Guttman-Yassky E. Understanding the immune landscape in atopic dermatitis: The era of biologics and emerging therapeutic approaches. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:756-68. doi: 10.1111/exd.13911.
- Torres T, Ferreira EO, Gonçalo M, Mendes-Bastos P, Selores M, Filipe P. Update on Atopic Dermatitis. Acta Med Port. 2019;32:606-13. doi: 10.20344/amp.11963.
- Grobe W, Bieber T, Novak N. Pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2019;17:433-40. doi: 10.1111/ddg.13819.
- Nomura T, Wu J, Kabashima K, Guttman-Yassky E. Endophenotypic Variations of Atopic Dermatitis by Age, Race, and Ethnicity. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8:1840-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.02.022.
- Brunner PM, Israel A, Zhang N, Leonard A, Wen HC, Huynh T, et al. Early-onset pediatric atopic dermatitis is characterized by TH2/TH17/TH22-centered inflammation and lipid alterations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:2094-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.040.
- Esaki H, Brunner PM, Renert-Yuval Y, Czarnowicki T, Huynh T, Tran G, et al. Early-onset pediatric atopic dermatitis is TH2 but also TH17 polarized in skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:1639-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.013.
- Flohr C, Johansson SG, Wahlgren CF, Williams H. How atopic is atopic dermatitis? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:150-8.
- Cork MJ, Danby SG, Vasilopoulos Y, et al. Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2009;129:1892-1908; doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.133.
- Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1483-94.
- Spergel JM, Paller AS. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112(6 Suppl):S118-27.
- Proksch E, Brandner JM, Jensen JM. The skin: an indispensable barrier. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17:1063-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00786.x.
- Madison KC. Barrier Function of the Skin: “La Raison d’Être” of the Epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;121:231-41. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12359.x.
- Kubo A, Nagao K, Amagai M. Epidermal barrier dysfunction and cutaneous sensitization in atopic diseases. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:440-7.
- Skabytska Y, Kaesler S, Volz T, Biedermann T. How the innate immune system trains immunity: lessons from studying atopic dermatitis and cutaneous bacteria. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:153-6. doi: 10.1111/ddg.12843.
- Sun L, Liu W, Zhang L. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Skin Host Defense, Psoriasis, and Atopic Dermatitis. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:1-13. doi: 10.1155/2019/1824624.
- Brandner J, Zorn-Kruppa M, Yoshida T, Moll I, Beck L, De Benedetto A. Epidermal tight junctions in health and disease. Tissue Barriers. 2015;3:e974451. doi: 10.4161/21688370.2014.974451.
- Kim BE, Leung DYM. Significance of Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018 May;10(3):207-215.
- Elias PM. The skin barrier as an innate immune element. Semin Immunopathol. 2007;29:3-14.
- Lee A-Y. Molecular Mechanism of Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction as Primary Abnormalities. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1194. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041194.
- Kubo A, Amagai M. Skin Barrier. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner A, et al., editors. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2019: 206-31.
- Igawa S, Kishibe M, Honma M, Murakami M, Mizuno Y, Suga Y, et al. Aberrant distribution patterns of corneodesmosomal components of tape-stripped corneocytes in atopic dermatitis and related skin conditions (ichthyosis vulgaris, Netherton syndrome and peeling skin syndrome type B). J Dermatol Sci. 2013;72:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.05.004.
- Trzeciak M, Sakowicz-Burkiewicz M, Wesserling M, Dobaczewska D, Glen J, Nowicki R, et al. Expression of Cornified Envelope Proteins in Skin and Its Relationship with Atopic Dermatitis Phenotype. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:36-41. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2482.
- Trzeciak M, Olszewska B, Sakowicz-Burkiewicz M, Sokołowska-Wojdyło M, Jankau J, et al. Expression Profiles of Genes Encoding Cornified Envelope Proteins in Atopic Dermatitis and Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas. Nutrients. 2020;12:862. doi: 10.3390/nu12030862.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Suárez-Fariñas M, Chiricozzi A, Nograles KE, Shemer A, Fuentes-Duculan J, et al. Broad defects in epidermal cornification in atopic dermatitis identified through genomic analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1235-44.e58. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.031.
- Carregaro F, Stefanini ACB, Henrique T, Tajara EH. Study of small proline-rich proteins (SPRRs) in health and disease: a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013;305:857-66. doi: 10.1007/s00403-013-1415-9.
- Kim BE, Leung DYM, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD. Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2 cytokines through –STAT-6. Clin Immunol. 2008;126:332-7.
- Howell MD, Kim BE, Gao P, Grant AV, Boguniewicz M, DeBenedetto A, et al. Cytokine modulation of atopic dermatitis filaggrin skin expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.07.012.
- Brown SJ, Irwin McLean WH. One Remarkable Molecule: Fi–laggrin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:751-62. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.393.
- Drislane C, Irvine AD. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease. Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.10.008.
- Kawasaki H, Nagao K, Kubo A, Hata T, Shimizu A, Mizuno H, et al. Altered stratum corneum barrier and enhanced percutaneous immune responses in filaggrin-null mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1538-46.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.068.
- Vávrová K, Henkes D, Strüver K, Sochorová M, Školová B, Witting MY, et al. Filaggrin Deficiency Leads to Impaired Lipid Profile and Altered Acidification Pathways in a 3D Skin Construct. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:746-53. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.402.
- Thyssen JP, Godoy-Gijon E, Elias PM. Ichthyosis vulgaris: the filaggrin mutation disease. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:1155-66. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12219.
- Rodríguez E, Baurecht H, Herberich E, Wagenpfeil S, Brown SJ, Cordell HJ, et al. Meta-analysis of filaggrin polymorphisms in eczema and asthma: Robust risk factors in atopic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:1361-70.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.03.03.
- Giardina E, Paolillo N, Sinibaldi C, Novelli G. R501X and 2282del4 Filaggrin Mutations Do Not Confer Susceptibility to Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis in Italian Patients. Dermatology. 2008;216:83-4. doi: 10.1159/000109365.
- Jurakic Toncic R, Kezic S, Jakasa I, Ljubojevic Hadzavdic S, Balic A, et al. Filaggrin loss-of-function mutations and levels of filaggrin degradation products in adult patients with atopic dermatitis in Croatia. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2020;34:1789-94. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16232.
- González-Tarancón R, Sanmartín R, Lorente F, Salvador-Rupérez E, Hernández-Martín A, Rello L, et al. Prevalence of FLG loss-of-function mutations R501X, 2282del4, and R2447X in Spanish children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:98-102. doi: 10.1111/pde.1402.
- Margolis DJ, Mitra N, Wubbenhorst B, D’Andrea K, Kraya AA, Hoffstad O, et al. Association of Filaggrin Loss-of-Function Variants With Race in Children With Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1269-76. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1946.
- Luukkonen T, Kiiski V, Ahola M, Mandelin J, Virtanen H, Pöyhönen M, et al. The Value of FLG Null Mutations in Predicting Treatment Response in Atopic Dermatitis: An Observational Study in Finnish Patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:456-63. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2578.
- Lowe AJ, Lee B, Orchard D, King E, Abramson MJ, Allen KJ, et al. Palm reading and water divining: A cross-sectional study of the accuracy of palmar hyperlinearity and transepidermal water loss to identify individuals with a filaggrin gene null mutation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1186-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.08.
- Leung DYM, Calatroni A, Zaramela LS, LeBeau PK, Dyjack N, Brar K, et al. The nonlesional skin surface distinguishes atopic dermatitis with food allergy as a unique endotype. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav2685.
- Esparza-Gordillo J, Weidinger S, Fölster-Holst R, Bauerfeind A, Ruschendorf F, Patone G, et al. A common variant on chromosome 11q13 is associated with atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet. 2009;41:596-601. doi: 10.1038/ng.347.
- Weidinger S, O’Sullivan M, Illig T, Baurecht H, Depner M, Rodriguez E, et al. Filaggrin mutations, atopic eczema, hay fever, and asthma in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:1203-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.014.
- Wu J, Guttman-Yassky E. Efficacy of biologics in ato–pic dermatitis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020;20:525-38. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1722998.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Bissonnette R, Ungar B, Suárez-Fariñas M, Ardeleanu M, Esaki H, et al. Dupilumab progressively improves systemic and cutaneous abnormalities in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:155-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.08.022.
- Pavel AB, Song T, Kim HJ, Del Duca E, Krueger JG, Dubin C, et al. Oral Janus kinase/SYK inhibition (ASN002) suppresses inflammation and improves epidermal barrier markers in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:1011-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.07.013.
- Ishida-Yamamoto A, Igawa S. The biology and regulation of corneodesmosomes. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;360:477-82. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2037-z.
- Rawlings AV, Voegeli R. Stratum corneum proteases and dry skin conditions. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351:217-35. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1501-x.
- Ishida-Yamamoto A, Igawa S, Kishibe M. Order and disorder in corneocyte adhesion. J Dermatol. 2011;38:645-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01227.
- Lee UH, Kim BE, Kim DJ, Cho YG, Ye YM, Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis is associated with reduced corneodesmosin expression: role of cytokine modulation and effects on viral penetration. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:537-40. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15010.
- Hatano Y, Adachi Y, Elias PM, Crumrine D, Sakai T, Kurahashi R, et al. The Th2 cytokine, interleukin-4, abrogates the cohesion of normal stratum corneum in mice: implications for pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:30-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12047.
- Furio L, Hovnanian A. Netherton syndrome: defective kallikrein inhibition in the skin leads to skin inflammation and allergy. Biol Chem. 2014;395:945-58. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0137.
- Cork MJ, Danby SG, Vasilopoulos Y, Hadgraft J, Lane ME, Moustafa M, et al. Epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009 Aug;129(8):1892-908. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.133. Epub 2009 Jun 4. PMID: 19494826.
- Zhao LP, Di Z, Zhang L, Wang L, Ma L, Lv Y, et al. Association of SPINK5 gene polymorphisms with atopic dermatitis in Northeast China. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2012;26:572-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04120.x.
- Kusunoki T, Okafuji I, Yoshioka T, Saito M, Nishikomori R, Heike T, et al. SPINK5 polymorphism is associated with disease severity and food allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:636-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.12.1114.
- Li Y, Li Y, Li W, Guo X, Zhou S, Zheng H. Genetic polymorphisms in serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 5 and risk of atopic dermatitis. Medicine. 2020;99:e21256. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021256.
- Voegeli R, Rawlings AV, Breternitz M, Doppler S, Schreier T, Fluhr JW. Increased stratum corneum serine protease activity in acute eczematous atopic skin. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:70-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09142.x.
- Nomura H, Suganuma M, Takeichi T, Kono M, Isokane Y, Sunagawa K, et al. Multifaceted analyses of epidermal serine protease activity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:913. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030913.
- Takai T. TSLP Expression: Cellular Sources, Triggers, and Regulatory Mechanisms. Allergol Int. 2012;61:3-17. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.11-RAI-0395.
- Wohlrab J, Gebert A, Neubert RH. Lipids in the Skin and pH. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2018;54:64-70. doi: 10.1159/000489519.
- Elias PM. Stratum Corneum Defensive Functions: An Integra–ted View. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:183-200. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23668.x.
- van Smeden J, Janssens M, Gooris GS, Bouwstra JA. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim Biophys Acta — Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2014;1841:295-313. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.11.006.
- Janssens M, van Smeden J, Gooris GS, Bras W, Portale G, Caspers PJ, et al. Lamellar lipid organization and ceramide composition in the stratum corneum of patients with atopic eczema. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:2136-8. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.175.
- Berdyshev E, Goleva E, Bronova I, Dyjack N, Rios C, Jung J, et al. Lipid abnormalities in atopic skin are driven by type 2 cytokines. JCI Insight. 2018;3:e98006. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.98006.
- Rabionet M, Gorgas K, Sandhoff R. Ceramide synthesis in the epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta — Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2014;1841:422-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.08.011.
- Boer DEC, van Smeden J, Al-Khakany H, Melnik E, van Dijk R, Absalah S, et al. Skin of atopic dermatitis patients shows disturbed β-glucocerebrosidase and acid sphingomyelinase activity that relates to changes in stratum corneum lipid composition. Biochim Biophys Acta — Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020;1865:158673. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158673.
- Pullmannová P, Pavlíková L, Kováčik A, Maixner J, Vávrová K. Permeability and microstructure of model stratum corneum lipid membranes containing ceramides with long (C16) and very long (C24) acyl chains. Biophys Chem. 2017;224:20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2017.03.004.
- Elias PM. Lipid abnormalities and lipid-based repair strategies in atopic dermatitis. Biochim Biophys Acta — Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2014;1841:323-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.001.
- Danso M, Boiten W, van Drongelen V, Gmelig Meijling K, Gooris G, El Ghalbzouri A, et al. Altered expression of epidermal lipid biosynthesis enzymes in atopic dermatitis skin is accompanied by changes in stratum corneum lipid composition. J Dermatol Sci. 2017;88:57-66.
- Toncic RJ, Jakasa I, Hadzavdic SL, Goorden SM, Vlugt KJG, Stet FS, et al. Altered levels of sphingosine, sphinganine and their ceramides in atopic dermatitis are related to skin barrier function, disease seve–rity and local cytokine milieu. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1958. doi: 10.3390/ ijms21061958.
- Hatano Y, Katagiri K, Arakawa S, Fujiwara S. Interleukin-4 depresses levels of transcripts for acid-sphingomyelinase and glucoce–rebrosidase and the amount of ceramide in acetone-wounded epidermis, as demonstrated in a living skin equivalent. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;47:45-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.02.010.
- Bäsler K, Bergmann S, Heisig M, Naegel A, Zorn-Kruppa M, Brandner JM. The role of tight junctions in skin barrier function and dermal absorption. J Control Release. 2016;242:105-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.08.007.
- Kubo A, Nagao K, Yokouchi M, Sasaki H, Amagai M. External antigen uptake by Langerhans cells with reorganization of epidermal tight junction barriers. J Exp Med. 2009;206:2937-46. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091527.
- Zaniboni MC, Samorano LP, Orfali RL, Aoki V. Skin barrier in atopic dermatitis: beyond filaggrin. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:472-8. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164412.
- Kezic S, Novak N, Jakasa I, Jungersted JM, Simon M, Brandner JM, et al. Skin barrier in atopic ermatitis. Front Biosci. 2014;19:542-56. doi: 10.2741/4225.
- Niessen CM. Tight Junctions/Adherens Junctions: Basic Structure and Function. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:2525-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700865.
- Benedetto A De, Rafaels NM, Mcgirt LY, Ivanov AI, Georas SN, Cheadle C, et al. Tight junction defects in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:773-86.
- Tokumasu R, Yamaga K, Yamazaki Y, Murota H, Suzuki K, Tamura A, et al. Dose-dependent role of claudin-1 in vivo in orchestrating features of atopic dermatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E4061-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525474113.
- Furuse M, Hata M, Furuse K, Yoshida Y, Haratake A, Sugitani Y, et al. Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier. J Cell Biol. 2002;156:1099-111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200110122.
- Gruber R, Börnchen C, Rose K, Daubmann A, Volksdorf T, Wladykowski E, et al. Diverse Regulation of Claudin-1 and Claudin-4 in Atopic Dermatitis. Am J Pathol. 2015;185:2777-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.06.021.
- Bergmann S, von Buenau B, Vidal-Y-Sy S, Haftek M, Wladykowski E, Houdek P, et al. Claudin-1 decrease impacts epidermal barrier function in atopic dermatitis lesions dose-dependently. Sci Rep. 2020;10:2024. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58718-9.
- Yuki T, Tobiishi M, Kusaka-Kikushima A, Ota Y, Tokura Y. Impaired Tight Junctions in Atopic Dermatitis Skin and in a Skin-Equivalent Model Treated with Interleukin-17. Koval M, ed. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161759.
- Asad S, Winge MC, Wahlgren CF, Bilcha KD, Nordenskjöld M, Taylan F, et al. The tight junction gene Claudin-1 is associated with atopic dermatitis among Ethiopians. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2016;30:1939-41. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13806.
- Yu HS, Kang MJ, Kwon JW, Lee SY, Lee E, Yang SI, et al. Claudin-1 polymorphism modifies the effect of mold exposure on the development of atopic dermatitis and production of IgE. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:827-30.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.040.
- De Benedetto A, Slifka MK, Rafaels NM, Kuo IH, Georas SN, Boguniewicz M, et al. Reductions in claudin-1 may enhance susceptibility to herpes simplex virus 1 infections in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:242-6.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.014.
- Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S. Pathogen Recognition by the Innate Immune System. Int Rev Immunol. 2011;30:16-34. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2010.529976.
- Chambers ES, Vukmanovic-Stejic M. Skin barrier immunity and ageing. Immunology. 2020;160:116-25. doi: 10.1111/imm.13152.
- Niyonsaba F, Kiatsurayanon C, Chieosilapatham P, Ogawa H. Friends or Foes? Host defense (antimicrobial) peptides and proteins in human skin diseases. Exp Dermatol. 2017;26:989-98. doi: 10.1111/exd.13314.
- Chieosilapatham P, Ogawa H, Niyonsaba F. Current insights into the role of human β-defensins in atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017;190:155-66. doi: 10.1111/cei.13013.
- Ong PY, Ohtake T, Brandt C, Strickland I, Boguniewicz M, Ganz T, et al. Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides and Skin Infections in Atopic Dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1151-60. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021481.
- Nomura I, Goleva E, Howell MD, Hamid QA, Ong PY, Hall CF, et al. Cytokine milieu of atopic dermatitis, as compared to psoriasis, skin prevents induction of innate immune response genes. J Immunol. 2003;171:3262-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3262.
- Hata TR, Kotol P, Boguniewicz M, Hata TR, Kotol P, Boguniewicz M, et al. History of eczema herpeticum is associated with the inability to induce human β-defensin (HBD)-2, HBD-3 and cathelicidin in the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:659-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09892.x.
- Rieg S, Steffen H, Seeber S, Humeny A, Kalbacher H, Stevanovic S, et al. Deficiency of dermcidin-derived antimicrobial peptides in sweat of patients with atopic dermatitis correlates with an impaired innate defense of human skin in vivo. J Immunol. 2005;174:8003-10. doi: 10.4049/ jimmunol.174.12.8003.
- Schwarz T. Immunology. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, editors. Dermatology. 4th Ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 81-99.
- Doherty TA, Broide DH. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells: new players in human allergic diseases. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2015;25:1-11.
- Bao K, Reinhardt RL. The differential expression of IL-4 and IL-13 and its impact on type-2 immunity. Cytokine. 2015;75:25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.008.
- Rafei-Shamsabadi DA, Klose CS, Halim TY, Tanriver Y, Jakob T. Context Dependent Role of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Skin Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02591.
- Brough HA, Nadeau KC, Sindher SB, Alkotob SS, Chan S, Bahnson HT, et al. Epicutaneous sensitization in the development of food allergy: What is the evidence and how can this be prevented? Allergy. 2020;75:2185-205. doi: 10.1111/all.14304.
- Wang V, Boguniewicz J, Boguniewicz M, Ong PY. The infectious complications of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.08.002.
- Williams MR, Gallo RL. The role of the skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015;15:65. doi: 10.1007/s11882-015-0567-4.
- Hill SE, Yung A, Rademaker M. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and antibiotic resistance in children with atopic dermatitis: A New Zealand experience. Australas J Dermatol. 2011;52:27-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2010.00714.x.
- Nakatsuji T, Chen TH, Narala S, Chun KA, Two AM, Yun T, et al. Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against Staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9:eaah4680. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aah4680.
- Kim J, Kim BE, Ahn K, Leung DY. Interactions between atopic dermatitis and Staphylococcus aureus infection: clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11:593-603. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.593.
- Feuillie C, Vitry P, McAleer MA, Kezic S, Irvine AD, Geoghegan JA, et al. Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to corneocytes from atopic dermatitis patients is controlled by natural moisturizing factor levels. MBio. 2018;9: e01184-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01184-18.
- Geoghegan JA, Irvine AD, Foster TJ. Staphylococcus aureus and atopic dermatitis: a complex and evolving relationship. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26:484-97. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.11.008.
- Kong HH, Oh J, Deming C, Conlan S, Grice EA, Beatson MA, et al. Temporal shifts in the skin microbiome associated with disease flares and treatment in children with atopic dermatitis. Genome Res. 2012;22:850-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.131029.111.
- Volz T, Skabytska Y, Guenova E, Chen KM, Frick JS, Kirschning CJ, et al. Nonpathogenic bacteria alleviating atopic dermatitis inflammation induce IL-10-producing dendritic cells and regulatory Tr1 Cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:96-104. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.291.
- Błazewicz I, Jaskiewicz M, Piechowicz L, Neubauer D, Nowicki RJ, Kamysz W, et al. Activity of antimicrobial peptides and conventional antibiotics against superantigen positive Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients with atopic dermatitis. Adv Dermatol Allergol. 2018;35:74-82. doi: 10.5114/ada.2018.62141.
- Gould HJ, Takhar P, Harries HE, Chevretton E, Sutton BJ. The Allergic March from Staphylococcus aureus Superantigens to Immunoglobulin E. In: Marone G, editor. Superantigens and Superallergens. Berlin: KARGER, 2007: 106-36. doi: 10.1159/000100861.
- Tsilochristou O, du Toit G, Sayre PH, Roberts G, Lawson K, Sever ML, et al. Association of Staphylococcus aureus colonization with food allergy occurs independently of eczema severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:494-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.04.025.
- Riechelmann H, Essig A, Deutschle T, Rau A, Rothermel B, Weschta M. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in house dust mite allergic patients and healthy controls. Allergy. 2005;60:1418-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00902.x.
- Shiomori T, Yoshida S, Miyamoto H, Makishima K. Relationship of nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus to pathogenesis of perennial allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:449-54. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.104256.
- Zeldin Y, Weiler Z, Cohen A, Kalinin M, Schlesinger M, Kidon M, et al. Efficacy of nasal Staphylococcus aureus eradication by topical nasal mupirocin in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;100:608-11. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60053-1.
- Jones AL, Curran-Everett D, Leung DYM. Food allergy is associated with Staphylococcus aureus colonization in children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:1247-1248. e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.01.010.
- Няньковський С.Л., Няньковська О.С., Яцула М.С., Городиловська М.І. Сучасні рекомендації щодо лікування атопічного дерматиту й харчової алергії в дітей. Здоров’я дитини. 2021. № 8. С. 520-528. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0551.16.8.2021.248707.
- Няньковський С.Л., Няньковська О.С., Городиловська М.І. Атопічний дерматит — актуальна проблема сучасної педіатрії. Здоров’я дитини. 2019. № 4. С. 250-255. DOI: 10.22141/2224-0551.14.4.2019.174039.
- Wollenberg A, Barbarot S, Bieber T, Christen-Zaech S, Deleuran M, Fink-Wagner A, et al.; European Dermatology Forum (EDF), the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV), the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI), the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis (ETFAD), European Federation of Allergy and Airways Diseases Patients’ Associations (EFA), the European Society for Dermatology and Psychiatry (ESDaP), the European Society of Pediatric Dermatology (ESPD), Global Allergy and Asthma European Network (GA2LEN) and the European Union of Medical Specialists (UEMS). Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) in adults and children: part I. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 May;32(5):657-682. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14891. Erratum in: J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Jul;33(7):1436. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15719. PMID: 29676534.
- Baron SE, Cohen SN, Archer CB, on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists and Royal College of General Practitioners, Guidance on the diagnosis and clinical management of atopic eczema. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 2012 May;37(Iss. s1, 1):7-12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04336.x.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, Krol A, Paller AS, Schwarzenberger K, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of ato–pic dermatitis: section 2. Management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Jul;71(1):116-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.023. Epub 2014 May 9. PMID: 24813302; –PMCID: PMC4326095.
- Stettler H еt al. Improved itch relief with new product formulation for topical treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis: results from an exploratory trial. Key Opinions in Medicine. 2016 Apr;11(Iss. 7).
- Proksch E et al. Topical use of dexpanthenol: a 70th anniversary article. Journal of Dermatological Treatment. 28:8:766-773.