Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 20, №7, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Кореляція між рівнем йоду і метаболізмом: огляд
Авторы: Le Zhang (1), Fangjian Shang (2), Cong Liu (1), Xiaodan Zhai (1)
(1) - Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
(2) - The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
Йод бере участь у синтезі гормонів щитоподібної залози і відіграє найважливішу роль у житті людини. Як дефіцит, так і надлишок йоду є поширеними проблемами серед певних груп населення. Йод також чинить екстратиреоїдну дію на органи, які можуть поглинати його незалежно від впливу гормонів щитоподібної залози. Нещодавні численні клінічні дослідження показали зв’язок між споживанням йоду і метаболічними розладами, такими як метаболічний синдром, ожиріння, цукровий діабет, артеріальна гіпертензія та дисліпідемія. Однак результати цих досліджень виявилися суперечливими, і механізми, що обумовлюють виявлені асоціації, досі недостатньо зрозумілі. Отже, мета даного огляду — проаналізувати результати нещодавніх досліджень щодо взаємозв’язку між йодом і метаболічними порушеннями, а також відповідні механізми.
Iodine is involved in the synthesis of thyroid hormones and plays a crucial role in human life. Both iodine deficiency and excess are common issues in certain populations. Iodine also has extrathyroidal effects on organs that can uptake it independently of thyroid hormones. Recently, multiple clinical studies have shown a connection between iodine intake and metabolic disorders, such as metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. However, the results of these studies have been inconsistent, and the mechanisms behind these associations are still not well understood. Therefore, in this review, we aim to examine the recent research progress regarding the relationship between iodine and metabolic disorders, along with the relevant mechanisms.
йод; метаболізм; ожиріння; дисліпідемія; антиоксиданти
iodine; metabolism; obesity; dyslipidemia; antioxidant
Вступ
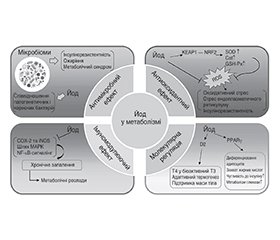
Молекулярна основа екстратиреоїдних ефектів йоду
Джерела й безпечна концентрація йоду
Клінічні дослідження кореляції між йодним статусом і метаболічними порушеннями
Йод і метаболічний синдром
Йод та ожиріння
Йод і гіперглікемія
Йод і гіпертензія
Йод і дисліпідемія
Йод і гіперурикемія та подагра
Йод і ризик смерті
Основні дослідження кореляції між йодом і метаболізмом
Екстратиреоїдні механізми йоду
Висновки
- De la Vieja A, Santisteban P. Role of iodide metabolism in physiology and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2018;25:R225-45. doi: 10.1530/erc-17-0515.
- Aceves C, Mendieta I, Anguiano B, Delgado-Gonzalez E. Molecular iodine has Extrathyroidal effects as an antioxidant, diffe–rentiator, and Immunomodulator. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:1228. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031228.
- Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemio–logy and prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; Ameri–can Heart Association; world heart federation; international atherosclerosis society; and International Association for the Study of obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640-5. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.109.192644.
- Saklayen MG. The global epidemic of the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018;20:12. doi: 10.1007/s11906-018-0812-z.
- Rani V, Deep G, Singh RK, Palle K, Yadav UC. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 2016;148:183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.02.002.
- Opazo MC, Coronado-Arrazola I, Vallejos OP, Moreno-Reyes R, Fardella C, Mosso L, et al. The impact of the micronutrient iodine in health and diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62:1466-79. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1843398.
- Leung AM, Braverman LE. Consequences of excess iodine. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10:136-42. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.251.
- Farebrother J, Zimmermann MB, Andersson M. Excess iodine intake: sources, assessment, and effects on thyroid function. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2019;1446:44-65. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14041.
- World Health Organization, United Nations Children’s Fund, International Council for Control of Iodine Deficiency Disorders. Progress towards the elimination of iodine deficiency disorders (IDD). WHO Booklet. World Health Organization, Geneva, 1999. Р. 1-33.
- Nagataki S. The average of dietary iodine intake due to the ingestion of seaweeds is 1.2 mg/day in Japan. Thyroid. 2008;18:667-8. doi: 10.1089/thy.2007.0379.
- Aceves C, Anguiano B, Delgado G. The extrathyronine actions of iodine as antioxidant, apoptotic, and differentiation factor in various tissues. Thyroid. 2013;23:938-46. doi: 10.1089/thy.2012.0579.
- Burgi H. Iodine excess. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;24:107-15. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2009.08.010.
- Cann SA, van Netten JP, van Netten C. Hypothesis: iodine, selenium and the development of breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 2000;11:121-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1008925301459.
- Smyth PP. Role of iodine in antioxidant defence in thyroid and breast disease. Biofactors. 2003;19:121-30. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520190304.
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2137-50. doi: 10.1200/jco.2005.05.2308.
- Inoue K, Leung AM, Sugiyama T, Tsujimoto T, Makita N, Nangaku M, et al. Urinary iodine concentration and mortality among U.S. adults. Thyroid. 2018;28:913-20. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0034.
- Maldonado-Araque C, Valdes S, Badia-Guillen R, Lago-Sampedro A, Colomo N, Garcia-Fuentes E, et al. Iodine deficiency and mortality in Spanish дорослих: Di@bet.es study. Thyroid. 2021;31:106-14. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0131.
- Mancini FR, Rajaobelina K, Dow C, Habbal T, Affret A, Balkau B, et al. High iodine dietary intake is associated with type 2 diabetes among women of the E3N-EPIC cohort study. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:1651-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.015.
- Park JK, Woo HW, Kim MK, Shin J, Lee YH, Shin DH, et al. Dietary iodine, seaweed consumption, and incidence risk of metabolic syndrome among postmenopausal women: a prospective analysis of the Korean multi-rural communities cohort study (MRCohort). Eur J Nutr. 2021;60:135-46. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02225-0.
- Neven KY, Cox B, Cosemans C, Gyselaers W, Penders J, Plusquin M, et al. Lower iodine storage in the placenta is associa–ted with gestational diabetes mellitus. BMC Med. 2021;19:47. doi: 10.1186/s12916-021-01919-4.
- Lee KW, Shin D, Song WO. Low urinary iodine concentrations associated with dyslipidemia in US adults. Nutrients. 2016;8:171. doi: 10.3390/nu8030171.
- Wang X, Xian T, Zhang L, Jia X, Man F, Liu L, et al. Associations between urinary iodine concentration, lipid profile and other cardiometabolic risk factors in adolescents: a cross-sectional, population-based ana–lysis. Br J Nutr. 2019;121:1039-48. doi: 10.1017/s0007114518003860.
- Liu J, Liu L, Jia Q, Zhang X, Jin X, Shen H. Effects of excessive iodine intake on blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipids in adults. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;192:136-44. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01668-9.
- Jin M, Zhang Z, Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, Ba J, et al. U-shaped associations between urinary iodine concentration and the prevalence of metabolic disorders: a crosssectional study. Thyroid. 2020;30:1053-65. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0516.
- Lu X, Shi X, Li Y, Chi H, Liao E, Liu C, et al. A negative association between urinary iodine concentration and the prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout: a crosssectional and population-based study in mainland China. Eur J Nutr. 2020;59:3659-68. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02199-z.
- Zhao J, Su Y, Zhang JA, Fang M, Liu X, Jia X, et al. Inverse association between iodine status and prevalence of metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional population-based study in a Chinese moderate iodine intake area. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:3691-701. doi: 10.2147/dmso.s322296.
- Ezemaduka Okoli CB, Woldu HG, Peterson CA. Low urinary iodine concentration is associated with increased risk for elevated plasma glucose in females: an analysis of NHANES 2011–12. Nutrients. 2021;13:4523. doi: 10.3390/nu13124523.
- Wang D, Wan S, Liu P, Meng F, Ren B, Qu M, et al. Associations between water iodine concentration and the prevalence of dyslipidemia in Chinese дорослих: a crosssectional study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;208:111682. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111682.
- Wang D, Wan S, Liu P, Meng F, Zhang X, Ren B, et al. Relationship between excess iodine, thyroid function, blood pressure, and blood glucose level in дорослих, pregnant women, and lactating women: a cross-sectional study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;208:111706. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111706.
- Villatoro-Santos CR, Ramirez-Zea M, Villamor E. Urinary sodium, iodine, and volume in relation to metabolic syndrome in Mesoamerican children and their parents. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022;32:1774-83. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.04.022.
- Kwak J, Hong G, Lee KJ, Kim CG, Shin D. Effect of the interaction between seaweed intake and LPL polymorphisms on metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults. Nutrients. 2023;15:2066. doi: 10.3390/nu15092066.
- Shan X, Liu C, Luo X, Zou Y, Huang L, Zhou W, et al. Iodine nutritional status and related factors among Chinese school-age children in three different areas: a crosssectional study. Nutrients. 2021;13:1404. doi: 10.3390/nu13051404.
- Lecube A, Zafon C, Gromaz A, Fort JM, Caubet E, Baena JA, et al. Iodine deficiency is higher in morbid obesity in comparison with late after bariatric surgery and non-obese women. Obes Surg. 2014;25:85-9. doi: 10.1007/s11695-014-1313-z.
- Aoe S, Yamanaka C, Ohtoshi H, Nakamura F, Fujiwara S. Effects of daily kelp (Laminaria japonica) intake on body composition, serum lipid levels, and thyroid hormone levels in healthy Japanese аdults: a randomized, double-blind study. Mar Drugs. 2021;19:352. doi: 10.3390/md19070352.
- Hitoe S, Shimoda H. Seaweed fucoxanthin supplementation improves obesity parameters in mild obese Japanese subjects. Funct Foods Health Dis. 2017;7:246-62. doi: 10.31989/ffhd.v7i4.333.
- Beer RJ, Herran OF, Villamor E. Median urinary iodine concentration in Colombian children and women is high and related to sociodemographic and geographic characteristics: results from a nationally representative survey. J Nutr. 2021;151:940-8. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa392.
- Al-Attas O, Al-Daghri N, Alkharfy K, Alokail M, Al-Johani N, Abd-Alrahman S, et al. Urinary iodine is associated with insulin resistance in subjects with diabetes mellitus type 2. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2012;120:618-22. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1323816.
- Kim MS, Kim JY, Choi WH, Lee SS. Effects of seaweed supplementation on blood glucose concentration, lipid profile, and antioxi–dant enzyme activities in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Res Pract. 2008;2:62-7. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2008.2.2.62.
- Bell GA, Mannisto T, Liu A, Kannan K, Yeung EH, Kim UJ, et al. The joint role of thyroid function and iodine concentration on gestational diabetes risk in a population-based study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:500-6. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13523.
- Cuellar-Rufino S, Navarro-Meza M, Garcia-Solis P, Xochihua-Rosas I, Arroyo-Helguera O. Iodine levels are associated with oxidative stress and antioxidant status in pregnant women with hypertensive disease. Nutr Hosp. 2017;34:661-6. doi: 10.20960/nh.460.
- Hata Y, Nakajima K, Uchida J-I, Hidaka H, Nakano T. Clinical effects of brown seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida (wakame), on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2001;30:43-53. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.30.43.
- Herter-Aeberli I, Cherkaoui M, El Ansari N, Rohner R, Stinca S, Chabaa L, et al. Iodine supplementation decreases hypercholesterolemia in iodine-deficient, overweight women: a randomized controlled trial. J Nutr. 2015;145:2067-75. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.213439.
- Shin D, Shim SR, Wu Y, Hong G, Jeon H, Kim CG, et al. How do Brown seaweeds work on biomarkers of dyslipidemia? A systematic review with Meta-analysis and Metaregression. Mar Drugs. 2023;21:220. doi: 10.3390/md21040220.
- Kroupova V, Kratochvil P, Kaufmann S, Kursa J, Travnicek J. Metabolic effect of iodine addition in laying hens. Vet Med. 2000;43:207-12.
- Xia Y, Qu W, Zhao LN, Han H, Yang XF, Sun XF, et al. Iodine excess induces hepatic steatosis through disturbance of thyroid hormone metabolism involving oxidative stress in BALB/c mice. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;154:103-10. doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9705-9.
- Zhao SJ, Ye Y, Sun FJ, Tian EJ, Chen ZP. The impact of dietary iodine intake on lipid metabolism in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011;142:581-8. doi: 10.1007/s12011-010-8767-1.
- Bocco B, Fernandes GW, Fonseca TL, Bianco AC. Iodine deficiency increases fat contribution to energy expenditure in male mice. Endocrinology. 2020;161:bqaa192. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa192.
- Rosique C, Lebsir D, Benatia S, Guigon P, Caire-Maurisier F, Benderitter M, et al. Metabolomics evaluation of repeated administration of potassium iodide on adult male rats. Arch Toxicol. 2020;94:803-12. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02666-w.
- Shen H, Han J, Li Y, Lu C, Zhou J, Li Y, et al. Different host-specific responses in thyroid function and gut microbiota modulation between diet-induced obese and normal mice given the same dose of iodine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019;103:3537-47. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09687-1.
- Li H, Chen S, Wu L, Wang H, Xiao K, Gao Y, et al. The effects of perineal disinfection on infant’s oral microflora after transvaginal –examination during delivery. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19:213. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2350-3.
- Vought RL, Brown FA, Sibinovic KH, McDaniel EG. Effect of changing intestinal bacterial flora on thyroid function in the rat. Horm Metab Res. 1972;4:43-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094095.
- Kupper FC, Carpenter LJ, McFiggans GB, Palmer CJ, Waite TJ, Boneberg EM, et al. Iodide accumulation provides kelp with an inorganic antioxidant impacting atmospheric chemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:6954-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709959105.
- Gutierrez-Repiso C, Velasco I, Garcia-Escobar E, Garcia-Serrano S, Rodriguez-Pacheco F, Linares F, et al. Does dietary iodine regulate oxidative stress and adiponectin levels in human breast milk? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20:847-53. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5554.
- Soriguer F, Gutierrez-Repiso C, Rubio-Martin E, Linares F, Cardona I, Lopez-Ojeda J, et al. Iodine intakes of 100–300 pg/d do not modify thyroid function and have modest anti-inflammatory effects. Br J Nutr. 2011;105:1783-90. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510005568.
- Arely RJ, Cristian AE, Omar AX, Antonio PJ, Isela SR, Yeimy Mar LR, et al. Iodine promotes glucose uptake through Akt phosphorylation and Glut-4 in adipocytes, but higher doses induce cytoto–xic effects in pancreatic Beta cells. Biology (Basel). 2024;13:26. doi: 10.3390/biology13010026.
- Bilal MY, Dambaeva S, Kwak-Kim J, Gilman-Sachs A, Beaman KD. A role for iodide and thyroglobulin in modulating the function of human immune cells. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1573. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01573.
- Honma K, Saga K, Onodera H, Takahashi M. Potassium iodide inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70:247-9. PMID: 1972841. doi: 10.2340/0001555570247249.
- Fernando IPS, Nah JW, Jeon YJ. Potential anti-inflammatory natural products from marine algae. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016;48:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.023.
- Barbalace MC, Malaguti M, Giusti L, Lucacchini A, Hre–lia S, Angeloni C. Antiinflammatory activities of marine algae in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3061. doi: 10.3390/ijms20123061.
- Schultze SM, Hemmings BA, Niessen M, Tschopp O. PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012;14:e1. doi: 10.1017/s1462399411002109.
- Mendieta I, Nunez-Anita RE, Nava-Villalba M, Zambrano-Estrada X, Delgado-Gonzalez E, Anguiano B, et al. Molecular iodine exerts antineoplastic effects by diminishing proliferation and invasive potential and activating the immune response in mammary cancer xenografts. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:261. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5437-3.
- Nunez-Anita RE, Arroyo-Helguera O, Cajero-Juarez M, Lopez-Bojorquez L, Aceves C. A complex between 6-iodolactone and the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor type gamma may mediate the antineoplastic effect of iodine in mammary cancer. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009;89:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.04.001.
- Nava-Villalba M, Nunez-Anita RE, Bontempo A, Aceves C. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is crucial for antitumoral effects of 6-iodolactone. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:168. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0436-8.
- Montaigne D, Butruille L, Staels B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18:809-23. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00569-6.
- Tepmongkol S, Keelawat S, Honsawek S, Ruangvejvorachai P. Rosiglitazone effect on radioiodine uptake in thyroid carcinoma patients with high thyroglobulin but negative total body scan: a correlation with the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Thyroid. 2008;18:697-704. doi: 10.1089/thy.2008.0056.
- Aceves C, Garcia-Solis P, Arroyo-Helguera O, Vega-Rive–roll L, Delgado G, Anguiano B. Antineoplastic effect of iodine in mammary cancer: participation of 6-iodolactone (6-IL) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR). Mol Cancer. 2009;8:33. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-33.
- Soriano O, Delgado G, Anguiano B, Petrosyan P, Molina-Servin ED, Gonsebatt ME, et al. Antineoplastic effect of iodine and iodide in dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced mammary tumors: association between lactoperoxidase and estrogen-adduct production. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011;18:529-39. doi: 10.1530/erc-11-0065.
- Olivo-Vidal ZE, Rodriguez RC, Arroyo-Helguera O. Iodine affects differentiation and migration process in trophoblastic cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;169:180-8. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0433-1.
- Bigoni-Ordonez GD, Ortiz-Sanchez E, Rosendo-Chalma P, Valencia-Gonzalez HA, Aceves C, Garcia-Carranca A. Molecular iodine inhibits the expression of stemness markers on cancer stem-like cells of established cell lines derived from cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:928. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4824-5.
- Moreno-Vega A, Vega-Riveroll L, Ayala T, Peralta G, Torres-Martel JM, Rojas J, et al. Adjuvant effect of molecular iodine in conventional chemotherapy for breast Cancer. Randomized pilot study. Nutrients. 2019;11:1623. doi: 10.3390/nu11071623.
- Li N, Jiang Y, Shan Z, Teng W. Prolonged high iodine intake is associated with inhibition of type 2 deiodinase activity in pituitary and elevation of serum thyrotropin levels. Br J Nutr. 2011;107:674-82. doi: 10.1017/s0007114511003552.
- Calil-Silveira J, Serrano-Nascimento C, Laconca RC, Schmiedecke L, Salgueiro RB, Kondo AK, et al. Underlying mecha–nisms of pituitary-thyroid Axis function disruption by chronic iodine excess in rats. Thyroid. 2016;26:1488-98. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0338.
- Sun X, Zhang X, Jiang Y, Bao S, Shan Z, Teng W. Expression of Iodotyrosine deiodinase in thyroid and other organs in iodine-deficient and iodine-excess rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015;167:272-9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0328-1.
- Bradley D, Liu J, Blaszczak A, Wright V, Jalilvand A, Needleman B, et al. Adipocyte DIO2 expression increases in human obesity but is not related to systemic insulin sensitivity. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:2464652-7. doi: 10.1155/2018/2464652.

/9.jpg)
/11.jpg)
/10.jpg)