Резюме
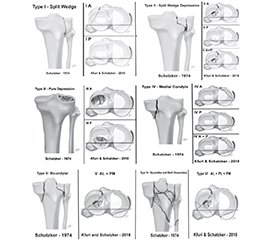
Актуальність. Переломи проксимального епіметафіза великогомілкової кістки становлять від 8,9 до 11 % випадків серед усіх переломів кісток гомілки і до 87 % — серед переломів у ділянці колінного суглоба. У даній групі переломи латерального виростка зустрічаються в 52–80 % випадків, медіального — в 7 %, а багатоуламкові переломи — у 41 %. Основним механізмом травми є варусне або вальгусне навантаження з осьовим перенавантаженням або без нього. Мета: провести аналіз сучасних способів оперативного лікування переломів проксимального епіметафіза великогомілкової кістки, визначити проблемні питання й перспективні шляхи їх вирішення. Матеріали та методи. Проведено аналіз літературних джерел з використанням бази даних Pubmed, UpToDate, Scopus, Web of Science, MEDLINE, The Cochrane Library, Embase, Global Health, пошук здійснювався за словами: «переломи проксимального епіметафіза великогомілкової кістки», «оперативне лікування». Результати. Загальноприйнятою класифікацією переломів проксимального епіметафіза великогомілкової кістки є класифікація AO/ASIF. Однак на практиці при визначенні типу перелому більш вживаною є класифікація J. Schatzker, R. McBroom, D. Bruce. Враховуючи сучасну концепцію трьох колон, J. Schatzker та співавт. доопрацювали свою класифікацію. Сучасні принципи лікування відображені в концепціях ORIF і МІРРО. Для стабілізації відламків використовуються гвинти, різноманітні пластини, відмінні за своїми конструктивними характеристиками, інтрамедулярні цвяхи й апарати зовнішньої фіксації. Висновки. Незважаючи на розробку ґрунтовних систематизованих підходів до лікування переломів проксимального епіметафіза великогомілкової кістки, які відображені в концепціях ORIF і МІРРО, залишаються невирішеними низка важливих питань. Дискусійними питаннями є: показання до оперативного й консервативного лікування; передопераційне планування; застосування типів фіксації та конструкцій, які забезпечать малоінвазивність і стабільність, що зумовлює необхідність подальших досліджень.
Background. Proximal tibial epimetaphysis fractures account for 8.9–11 % of all tibial fractures and up to 87 % of fractures in the knee joint. In the latter group, lateral condyle fractures occur in 52 to 80 % of cases, medial condyle fractures — in up to 7 %, and comminuted fractures — in 41 % of patients. The main mechanism of injury is varus or valgus loading with or without axial overload. Purpose: to analyze modern methods of surgical treatment for proximal tibial epimetaphysis fractures, to identify problematic issues and promising ways to solve them. Material and methods. Literature sources were analyzed in the following databases: Pubmed, UpToDate, Scopus, Web of Science, MEDLINE, The Cochrane Library, Embase, Global Health using the search terms: “proximal tibial epimetaphysis fractures”, “surgical treatment”. Results. The AO/ASIF classification is considered to be the generally accepted classification of the proximal tibial epimetaphysis fractures. However, when determining the type of fracture, classification of J. Schatzker, R. McBroom, D. Bruce is more commonly used. Given the modern three-column concept, J. Schatzker and co-authors have finalized their classification. Current treatment principles are represented by the ORIF and MIPPO concepts. To stabilize the fragments, one can use screws, plates with various design characteristics, intramedullary nails and external fixation devices. Conclusions. Despite the development of thorough systematized approaches to the treatment of the proximal tibial epimetaphy-sis fractures, represented by the ORIF and MIPPO concepts, some crucial issues remain unresolved. Controversial issues include indications for surgical and conservative treatment; preoperative planning; use of fixation types and structures that will be minimally invasive and stable, which necessitates further research.
Список литературы
1. Bormann М, Neidlein С, Gassner С et al. Changing patterns in the epidemiology of tibial plateau fractures: a 10-year review at a level-I trauma center. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023;49(1):401-409. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-02076-w.
2. Donovan RL, Smith JRA, Yeomans D еt al. Epidemiology and outcomes of tibial plateau fractures in adults aged 60 and over treated in the United Kingdom. Injury. 2022;53(6):2219-2225. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.03.048.
3. Lv H, Zhang Q, Chen W et al. Epidemiological Study of Tibial Plateau Fractures Combined with Intercondylar Eminence Fractures. Orthopaedic Surgery. 2020;12(2):561-569. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12658.
4. Porrino J, Richardson ML, Hovis К et al. Association of Tibial Plateau Fracture Morphology With Ligament Disruption in the Context of Multiligament Knee Injury. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2018;47(6):410-416. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2017.09.001.
5. Le Baron M, Cermolacce M, Flecher X et al. Tibial plateau fracture management: ARIF versus ORIF — clinical and radiological comparison. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(1):101-106. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2018.10.015.
6. Gicquel T, Najihi N, Vendeuvre T et al. Tibial plateau fractures: Reproducibility of three classifications (Schatzker, AO, Duparc) and a revised Duparc classification. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research. 2013;805-816. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2013.06.007.
7. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968–1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979 Jan-Feb;(138):94-104.
8. Kfuri M, Schatzker J. Revisiting the Schatzker classification of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2018;49:2252-63. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.11.010.
9. Schatzker J, Kfuri M. Revisiting the management of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2022;53(6):2207-2218. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.04.006.
10. Chang H, Zheng Z, Shao D, Yu Y, Hou Z, Zhang Y. Incidence and radiological predictors of concomitant meniscal and cruciate ligament injuries in operative tibial plateau fractures: a prospective diagnostic study. Sci Rep. 2018;8:13317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31705-x.
11. Yan В, Sun J, Yin W. The prevalence of soft tissue injuries in operative Schatzker type IV tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(8):1269-1275. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03533-0.
12. Hinterwimmer S, Kanz KG, Hinterwimmer S. Gultigkeitsprufung der Ottawa Knee Rules fur Standard-Rontgenaufhahmen bei akuten Knieverletzungen. Unfall Chirurg. 2002;05(7):624-626. doi: 10.1007/s00113-002-0421-8.
13. Mattijssen-Horstink L, Joëlle Langeraar J, van der Stappen W еt al. Radiologic discrepancies in diagnosis of fractures in a Dutch teaching emergency department: a retrospective analysis. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine. 2020;28(38).
14. Assink N, Kraeima J, Slump CH et al. Quantitative 3D measurements of tibial plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):14395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50887-6.
15. MacKay JW, Murray PJ, Kasmai B, Johnson G, Donell ST, Toms AP. MRI texture analysis of subchondral bone at the tibial plateau. Eur Radiol. 2016;26:3034-3045. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-4142-0.
16. Nikolopoulos D, Michos J, George K. Safos Tibia Patho–logy and Fractures. 2020;144. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.87317.
17. Booth FW. Physiologic and Biochemical Effects of immobilization on Muscle. Clin Orthop. 1987;219:21-27.
18. Mthethwa J, Chikate A. A review of the management of tibial plateau fractures. Musculoskelet Surg. 2018;102(2):119-27. doi: 10.1007/s12306-017-0514-8.
19. Liu ZY, Zhang JL, Liu C et al. Surgical Strategy for Anterior Tibial Plateau Fractures in Hyperextension Knee Injuries. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3):966-978. doi: 10.1111/os.12997.
20. Shen QJ, Xing GS, Liu ZY et al. Surgical treatment of the complex bicondylar tibial plateau fracture using a midline longitudinal incision]. 2020;100(16):1260-1263. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20190904-01962.
21. Canton G, Sborgia А, Dussi M et al. Early weight bea–ring in tibial plateau fractures treated with ORIF: a systematic review of literature. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 2022;17(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03156-8.
22. Rudran B, Little C, Wiik A et al. Tibial plateau fracture: anatomy, diagnosis and management. Br J Hosp Med. 2020;81(10):1-9. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2020.0339.
23. Forna N, Sîrbu P-D. Epidemiological features and osteosynthesis methods: a clinical study on 63 patients with tibial plateaus fractures. Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation. 2022;14(1):102-113.
24. Mohandes Y, Tahani M, Rouhi G et al. Osteosynthesis of diaphyseal tibia fracture with locking compression plates: A numerical investigation using Taguchi and ANOVA. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(12):3528. doi: 10.1002/cnm.3528.
25. Parhamfar M, Mohammadsharifi G, Taravati A. The Comparison Between 3.5- and 4.5-mm T-plates for Management of the Patients with Schatzker Type II Tibial Plateau Fractures that Referred to our Emergency Department: A Clinical Trial. Biomed Res. 2023;12:206. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_40_23.
26. Biggi F, Di Fabio S, D’Antimo C et al. Tibial plateau fractures: internal fixation with locking plates and the MIРPO technique. Injury. 2010;41(11):1178-82. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.08.001.
27. Meena DK, Choubisa R, Sharma A et al. Comprehensive analysis of locking compression plate (LCP) treatment for proximal tibia fractures: utilizing minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technigue and assessing clinical outcomes, complication, and fixation strategies. Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology. 2021:28(2):237-243. doi: 10.53555/jptcp.v28i2.3660.
28. Mónico JL, Andrade R, Matos P. Tibial plateau fractures osteosynthesis — a case series of 88 patients evaluating surgical approaches, results and complications. Annals of Joint. 2021;6. doi: 10.21037/aoj-20-95.
29. Oleo-Taltavull R, Corró S, Tomàs-Hernández J. et al. Staged treatment of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: influence of frame configuration and quality of reduction on outcomes. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023;18. doi: 10.1007/s00068-023-02411-9.
30. Kulkarni MS, Tummala M, Aroor MN et al. Suprapatellar nailing in proximal third tibial fractures-clinicoradiological outcome. Injury. 2020;51(8):1879-1886. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2020.05.008.
31. Tripathy SK, Varghese P, Panigrahi S et al. External fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation in the treatment of Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021;55(5):444-456. doi: 10.5152/j.aott.2021.20350.
32. Jabara JT, Only AJ, Paull TZ et al. Arthroscopically Assisted Percutaneous Screw Fixation of Tibial Plateau Fractures. JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques. 2022;12(2):e21.00026. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.21.00026.
33. Dhillon MS, Virk MS, Kumar P et al. The effectiveness of arthroscopy assisted fixation of Schatzker types I-III tibial plateau fractures: our experience at a tertiary centre. Int J Burns Trauma. 2021;11(3):163-169.
34. Li C, Chen Z. Diagnostic value of X-ray and CT combined with MRI in tibial plateau fracture. Journal of Molecular Imaging. 2020;43(1):122-125. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2020.01.25.
35. Liu XD, Wang HB, Zhang TC et al. Comparison between computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in clinical diagnosis and treatment of tibial platform fractures. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(18):4067-4074. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4067.
36. Singleton N, Sahakian V, Muir D. Outcome after tibial plateau fracture: how important is restoration of articular congruity? J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31:158-163. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000762.
37. Jeelani A, Arastu MH. Tibial plateau fractures — review of current concepts in management. Orthop Trauma. 2017;31:102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.mporth.2016.10.005.
38. Vaartjes T, Assink N, Nijveldt R et al. Functional Outcome After Nonoperative Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures in Skeletally Mature Patients: What Sizes of Gaps and Stepoffs Can be Accepted? Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2022;480(12):2288-2295. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002266.
39. Giordano V, Belangero WD, Sá BA et al. Plate-screw and screw-washer stability in a Schatzker type-I lateral tibial plateau fracture: a comparative biomechanical study. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2020;47:e20202546. doi: 10.1590/0100-6991e-20202546.
40. Belaid D, Delmon R, Aubert K et al. Biomechanical study between 4.5 mm and 3.5 mm distal locking screws in tibial plateau fractures. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering. 44th Congress of the Société de Biomécanique. 2019;22(1):430-431. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2020.1714970.
41. Ferre S, Di Nisio FG, Mendonça CJA et al. Comparative analysis of tibial plateau fracture osteosynthesis: A finite element study. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 2022;134:105392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2022.105392.
42. Georgiadis GM. Combined anterior and posterior approaches for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994;76:285-289.
43. Gahr P, Mittlmeier T, Grau A et al. Functional assessment and outcome following surgical treatment of displaced tibial plateau fractures: a retrospective analysis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023;49(6):2373-2379. doi: 10.1007/s00068-023-02401-x.