Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 21, №1, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив застосування вакуум-терапії та інстиляції L-аргініну при лікуванні гнійних ран на активність ферментів циклу оксиду азот
Авторы: T.V. Horodova-Andrieieva, O.Ye. Akimov, V.O. Kostenko, O.H. Krasnov, V.I. Lyakhovskyi, M.I. Kravtsiv
Poltava State Medical University, Poltava, Ukraine
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Проблема лікування гнійних ран залишається однією з найактуальніших за всю історію хірургії. У наш час, незважаючи на багаторічний досвід і постійні наукові дослідження, проблема діагностики й лікування гнійних ран не втрачає своєї актуальності. Мета: оцінити вплив вакуум-терапії та інстиляції L-аргініну при лікуванні гнійної рани на продукцію оксиду азоту різними ізоформами NO-синтази та активність аргіназного шляху метаболізму L-аргініну.
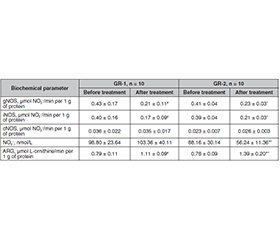
Матеріали та методи. В експерименті взяли участь 20 пацієнтів, які були рандомізовано розподілені на 2 групи: вакуумної терапії (GR-1, n = 10) та вакуумної терапії з інстиляціями розчину L-аргініну (GR-2, n = 10). У плазмі крові досліджували наступні параметри: загальну активність NO-синтази, активність індуцибельної та конститутивної ізоформ NO-синтази, активність аргіназ і концентрацію нітритів. Результати. При порівнянні результатів, отриманих після лікування гнійної рани в пацієнтів GR-1 і GR-2, виявлено статистично значущу різницю в концентрації нітритів і активності аргіназ. Так, концентрація нітритів у венозній крові хворих GR-2 була на 45,59 % нижчою, ніж у пацієнтів GR-1. Активність аргінази в плазмі крові, взятій із найближчого до гнійної рани венозного русла, у GR-2 була на 25,23 % вищою порівняно з показниками GR-1. Висновки. Вакуумна терапія з інстиляцією L-аргініну, крім ефектів власне такої терапії, обмежує накопичення нітритів у крові венозного русла, найближчого до місця гнійної рани, та посилює утилізацію L-аргініну аргіназним шляхом.
Background. The problem of treating purulent wounds remains one of the most urgent throughout the history of surgery. Nowadays, despite many years of experience and constant scientific research, the problem of diagnosis and treatment of purulent wounds does not lose its relevance. The purpose is to evaluate the effect of vacuum therapy and instillation of L-arginine in the treatment of a purulent wound on the production of nitric oxide by different isoforms of NO-synthase and the activity of the arginase pathway of L-arginine metabolism. Materials and methods. The experiment was conducted in 20 patients who were randomly divided into 2 groups: vacuum therapy (GR-1, n = 10) and vacuum therapy with instillations of L-arginine solution (GR-2, n = 10). In the blood plasma, the following parameters were investigated: total activity of NO-synthase, activity of the inducible and constitutive isoforms of NO-synthase, activity of arginases and nitrite concentration. Results. When comparing the results obtained after the treatment of a purulent wound in patients from GR-1 and GR-2, a statistically significant difference was found in the concentration of nitrites and the activity of arginases. Thus, the concentration of nitrites in the venous blood of GR-2 patients after treatment of a purulent wound was 45.59 % lower than in GR-1. The activity of arginase in the blood plasma taken from the venous bed closest to a purulent wound was 25.23 % higher in patients with GR-2 compared to the indicators in GR-1. Conclusions. Vacuum therapy with L-arginine instillation, in addition to the effects of therapy itself, limits the accumulation of nitrites in the blood of the venous bed closest to a purulent wound and enhances the metabolism of L-arginine by the arginase pathway.
гнійні рани; оксид азоту; L-аргінін; вакуумна терапія; NO-синтаза; аргіназа
purulent wounds; nitric oxide; L-arginine; vacuum therapy; NO-synthase; arginase
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Jakanov MK, Zhakiev BS, Karsakbayev UG, Kurmanbayev BA, Taishibayev KR, Sagynganov SK. Endovascular surgery for the treatment of purulent and necrotic complications in diabetic foot syndrome. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021;35:106. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.35.106.
- Shaprynskyi VO, Skalskyi SS, Shaprynskyi YV, Verba AV, Makarov VM. Complex treatment of purulent wounds with the use of high-pressure aerodisperse mixture. Wiad Lek. 2020;73(5):889-894.
- Daher GS, Choi KY, Wells JW, Goyal N. A systematic review of oral nutritional supplement and wound healing. Ann Otol Rhinol Lary-ngol. 2022;131(12):1358-1368. doi: 10.1177/00034894211069437.
- Akimov OYe, Kostenko VO. Functioning of nitric oxide cycle in gastric mucosa of rats under excessive combined intake of sodium nitrate and fluoride. Ukr Biochem J. 2016;88(6):70-75. doi: 10.15407/ubj88.06.070.
- Matsytska YK, Akimov OY, Mykytenko AO. Influence of corvitin and metformin on biochemical changes in lacrimal glands of rats during water avoidance stress modeling. Oftalmologicheskii Zhurnal. 2022;97(3):39-44. doi: 10.31288/oftalmolzh202233944.
- Fitzsimmons LF, Clark TR, Hackstadt T. Nitric oxide inhibition of Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 2021;89(12):e0037121. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00371-21.
- Li Y, Liu X, Cui Z, Zheng Y, Jiang H, Zhang Y, et al. Trea-ting multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections by functionalized nano-bismuth sulfide through the synergy of immunotherapy and bacteria-sensitive phototherapy. ACS Nano. 2022;16(9):14860-14873. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c05756.
- Yi K, Yang Y, Yuan Y, Xiang Y, Zhou S. Impaired autophagy causes severe corneal neovascularization. Cells. 2022;11(23):3895. doi: 10.3390/cells11233895.
- Alhalwani AY, Davey RL, Kaul N, Barbee SA, Huffman J.A. Modification of lactoferrin by peroxynitrite reduces its antibacterial activity and changes protein structure. Proteins. 2020;88(1):166-174. doi: 10.1002/prot.25782.
- Beam JE, Wagner NJ, Shook JC, Bahnson ESM, Fow-ler VG Jr, Rowe SE, et al. Macrophage-produced peroxynitrite induces antibiotic tolerance and supersedes intrinsic mechanisms of persister formation. Infect Immun. 2021;89(10):e0028621. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00286-21.
- Borisov VB, Siletsky SA, Paiardini A, Hoogewijs D, Forte E, et al. Bacterial oxidases of the cytochrome bd family: Redox enzymes of unique structure, function, and utility as drug targets. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021;34(16):1280-1318. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8039.
- Szondi DC, Wong JK, Vardy LA, Cruickshank SM. Arginase signalling as a key player in chronic wound pathophysio-logy and healing. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:773866. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.773866.
- Denans N, Tran NTT, Swall ME, Diaz DC, Blanck J, Piotrowski T. An anti-inflammatory activation sequence governs macrophage transcriptional dynamics during tissue injury in zebrafish. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5356. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33015-3.
- Crompton RA, Williams H, Campbell L, Hui Kheng L, Sa–ville C, Ansell DM, et al. An epidermal-specific role for Arginase1 during cutaneous wound repair. J Invest Dermatol. 2022;142(4):1206-1216.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.09.009.
- Carriche GM, Almeida L, Stüve P, Velasquez L, Dhillon-LaBrooy A, Roy U, et al. Regulating T-cell differentiation through the polyamine spermidine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;147(1):335-348.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.037.
- Almeida L, Dhillon-LaBrooy A, Carriche G, Berod L, Sparwasser T. CD4+ T-cell differentiation and function: Unifying glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, polyamines NAD mitochondria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148(1):16-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.03.033.
- Duprey A, Groisman EA. DNA supercoiling differences in bacteria result from disparate DNA gyrase activation by polyamines. PLoS Genet. 2020;16(10):e1009085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009085.
- Douglas EJA, Alkhzem AH, Wonfor T, Li S, Woodman TJ, et al. Antibacterial activity of novel linear polyamines against Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:948343. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.948343.
- Zhu W, Dong Y, Xu P, Pan Q, Jia K, Jin P, et al. A composite hydrogel containing resveratrol-laden nanoparticles and platelet-derived extracellular vesicles promotes wound healing in diabetic mice. Acta Biomater. 2022;154:212-230. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.10.038.
- Veerasubramanian PK, Joe VC, Liu WF, Downing TL. Cha–racterization of macrophage and cytokine interactions with biomaterials used in negative-pressure wound therapy. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021;9(1):2. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9010002.
- Song H, Xu Y, Chang W, Zhuang J, Wu X. Negative pressure wound therapy promotes wound healing by suppressing macrophage inflammation in diabetic ulcers. Regen Med. 2020;15(12):2341-2349. doi: 10.2217/rme-2020-0050.
- Wang Y, Wei W, Han Y. Effect of decellularized adipose tissue combined with vacuum sealing drainage on wound inflammation in pigs. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(3):373-381. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201904010.
- Feng Y, Feng Y, Gu L, Liu P, Cao J, Zhang S. The critical role of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) metabolism in modulating radiosensitivity: BH4/NOS axis as an angel or a devil. Front Oncol. 2021;11:720632. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.720632.
- Zhang H, Jin Y, Wang M, Loor JJ, Wang H. N-Carbamylglutamate and l-arginine supplementation improve hepatic antioxidant status in intrauterine growth-retarded suckling lambs. RSC Adv. 2020;10(19):11173-11181. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09316h.
- Huang J, Ladeiras D, Yu Y, Ming XF, Yang Z. Detrimental effects of chronic L-arginine rich food on aging kidney. Front Pharmacol. 2021;11:582155. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.582155.
- Mariotti F. Arginine supplementation and cardiometabo-lic risk. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2020;23(1):29-34. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000612.
- Szefel J, Danielak A, Kruszewski WJ. Metabolic pathways of L-arginine and therapeutic consequences in tumors. Adv Med Sci. 2019;64(1):104-110. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2018.08.018.
- Abd El-Aleem SA, Abd-Elghany MI, Ali Saber E, Jude EB, Djouhri L. A possible role for inducible arginase isoform (AI) in the pathogenesis of chronic venous leg ulcer. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(12):9974-9991. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29812.
- Lin WT, Yang SC, Tsai SC, Huang CC, Lee NY. L-Arginine attenuates xanthine oxidase and myeloperoxidase activities in hearts of rats during exhaustive exercise. Br J Nutr. 2006;95(1):67-75. doi: 10.1079/bjn20051602.
- Gee LC, Massimo G, Lau C, Primus C, Fernandes D, Chen J, et al. Inorganic nitrate attenuates cardiac dysfunction: roles for xanthine oxidoreductase and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(20):4757-4777. doi: 10.1111/bph.15636.
- Mykytenko AO, Akimov OY, Yeroshenko GA, Neporada KS. Influence of NF-κB on the development of oxidative-nitrosative stress in the liver of rats under conditions of chronic alcohol intoxication. Ukr Biochem J. 2022;94(6):57-66. doi: 10.15407/ubj94.06.057.
- Mykytenko AO, Akimov OY, Yeroshenko GA, Neporada KN. Influence of doxorubicin on the extracellular matrix of the liver of rats under conditions of chronic alcoholic hepatitis. Regulatory Mechanisms in Biosystems. 2023;14(2):278-283. doi: 10.15421/022341.