Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №2, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Комплексне лікування пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом типу 2, ускладненим діабетичною хворобою нирок, із супутнім неалкогольним стеатогепатитом
Авторы: Z.Ya. Kotsiubiichuk, А.А. Antoniv, O.V. Kaushanska, L.V. Kanovska, Yu.M. Yarinich
Bukovinian State University, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
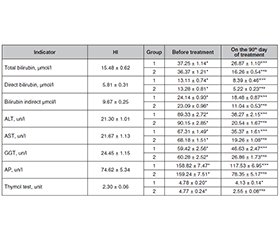
Мета дослідження: встановити вплив біциклолу на клінічні прояви неалкогольного стеатогепатиту (НАСГ), маркери пошкодження печінки у хворих на неалкогольний стеатогепатит та цукровий діабет 2-го типу (ЦД2), ступінь стеатозу гепатоцитів і стадію фіброзу печінки. Матеріали та методи. Проведено дослідження в динаміці лікування 60 хворих на НАСГ із ЦД2 середнього ступеня тяжкості, з них у 15 осіб (25,0 %) ЦД2 був у стані компенсації, у 45 (75,0 %) — субкомпенсований. Крім ЦД2, у пацієнтів iз НАСГ на момент включення в дослідження не виявлено іншої хронічної соматичної патології в активній фазі або в стані декомпенсації (серця, судин, нирок, органів травлення, системи крові та кровотворення, неврологічних, психічних, онкологічних, ендокринних, ревматичних хвороб, жирової дистрофії печінки алкогольної етіології), гострих захворювань, вагітності, лактації. Результати. Лікування біциклолом виявилося більш ефективним порівняно з традиційною терапією (есенціальні фосфоліпіди) за рахунок зниження інтенсивності клінічних синдромів неалкогольного стеатогепатиту: астеновегетативного, абдомінального дискомфорту, диспепсії, гепатомегалії (p < 0,05), а також активності біохімічних синдромів: цитолізу, холестазу, мезенхімального запалення (p < 0,05); воно також зменшувало стеатоз (p < 0,05) і сприяло зворотному розвитку фіброзу печінки (p < 0,05). У хворих обох груп порівняння після лікування вірогідно зменшилися прояви диспепсії: зникли нудота, відрижка повітрям, здуття живота. Так, після терапії кількість пацієнтів із симптомами диспепсії в першій групі знизилась в 1,3 раза (p > 0,05). Висновки. Лікування біциклолом ефективніше традиційної терапії неалкогольного стеатогепатиту на тлі цукрового діабету 2-го типу і може бути рекомендовано як терапія першої лінії протягом трьох місяців 1 або 2 рази на рік.
Background. The purpose of research is to establish the effect of bicyclol on the clinical manifestations of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), markers of liver damage in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2), the degree of hepatocyte steatosis and the stage of liver fibrosis. Materials and methods. Studies were carried out in the dynamics of treatment in 60 patients with NASH with DM2 of moderate severity, of which 15 people (25.0 %) had DM2 in the compensatory stage, 45 (75.0 %) — subcompensated. Besides DM2, at the time of inclusion in the study patients with NASH had no other chronic somatic pathology in the active phase or in the stage of decompensation (heart, vascular, kidney, digestive system, blood and hematopoiesis, neurological, psychiatric, cancer, endocrine, rheumatic diseases, fatty liver disease of alcoholic origin), acute illnesses, pregnancy, lactation. Results. Bicyclol treatment was more effective than traditional therapy (essential phospholipids) due to reducing the severity of clinical syndromes of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: astheno-vegetative, abdominal discomfort, dyspepsia, hepatomegaly (p < 0.05), as well as the activity of biochemical syndromes: cytolysis, cholestasis, mesenchymal inflammation (p < 0.05); it also decreased steatosis (p < 0.05), and contributed to the reversal of liver fibrosis (p < 0.05). In patients of both comparison groups, dyspepsia manifestations reduced significantly after treatment: nausea, belching, bloating disappeared. Thus, the number of patients with the symptoms of dyspepsia in group 1 decreased by 1.3 times after therapy (p > 0.05). Conclusions. Bicyclol treatment is more effective than traditional therapy for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis on the background of diabetes mellitus type 2 and may be recommended for use as first-line therapy for 3 months one or two times a year.
неалкогольний стеатогепатит; цукровий діабет типу 2; лікування; біциклол
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; type 2 diabetes mellitus; treatment; bicyclol
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Tang J, Gu J, Chu N, Chen Y, Wang Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of bicyclol for treating patients with idiosyncratic acute drug-induced liver injury: A multicenter, randomized, phase II trial. Liver Int. 2022 Aug;42(8):1803-1813. doi: 10.1111/liv.15290.
- Du Y, Gu J, Yang Y, Chen Y, Wang Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of bicyclol for treating patients with antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2024 Jan 1;28(1):6-12. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.23.0038.
- Tokushige K, Ikejima K, Ono M, Eguchi Y, Kamada Y, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 2020. Hepatol Res. 2021 Oct;51(10):1013-1025. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13688.
- Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, Abdelma–lek MF, Caldwell S, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-1835. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000323.
- Zhao T, Mao L, Yu Z, Hui Y, Feng H, et al. Therapeutic potential of bicyclol in liver diseases: Lessons from a synthetic drug based on herbal derivative in traditional Chinese medicine. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Feb;91:107308. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107308.
- Wang Y, Lai R, Zong P, Xu Q, Shang J, et al. Bicyclol for the treatment of drug-induced liver injury: a propensity score matching analysis using a nationwide inpatient database. J Int Med Res. 2021 Apr;49(4):3000605211005945. doi: 10.1177/03000605211005945.
- Li XL, Cui JJ, Zheng WS, Zhang JL, Li R, et al. Bicyclol alleviates atherosclerosis by manipulating gut microbiota. Small. 2022 Mar;18(9):e2105021. doi: 10.1002/smll.202105021.
- Zhao W, Yan Y, Xiao Z, Wang M, Xu M, et al. Bicyclol ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via inhibiting MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Sep;141:111874. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111874.
- Li M, Liu GT. Inhibition of Fas/FasL mRNA expression and TNF-α release in concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice by bicyclol. WJG. 2004;10(12):1775-1779. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i12.1775.
- Li H, Liu NN, Li JR, Wang MX, Tan JL, et al. Bicyclol ameliorates advanced liver diseases in murine models via inhibiting the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jun;150:113083. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113083.
- Naqiong W, Liansheng W, Zhanying H, et al. A multicenter and randomized controlled trial of bicyclol in the treatment of statin-induced liver injury. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:5760-5766. doi: 10.12659/msm.904090.
- Shang W, Feng Y, Li J, et al. Effect of bicyclol tablets on drug-induced liver injuries after kidney transplantation. Open Medi–cine. 2017;12(1):62-69. doi: 10.1515/med-2017-0012.
- Wang HF, Li Q, Lan P. Use of bicyclol in treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2007;21(2):165-167.
- Wang Y, Nie H, Zhao X, et al. Bicyclol induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the PI3K/AKT and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathways. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:742. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2767-2.
- Xie W, Shi G, Zhang H, et al. A randomized, multicenter, controlled study of patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic he–patitis B treated by adefovir dipivoxil or adefovir dipivoxil plus bicyclol. Hepatol Int. 2012;6(2):441-448. doi: 10.1007/s12072-011-9294-7.
- Yang XY, Zhuo Q, Wu TX, Liu GJ. Bicyclol for chronic hepatitis C. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(1):CD004994.
- Yi J, Lianhua L, Zeng L, et al. Effect of bicyclol on TGF-β1 and I, III collagen expression in liver tissue of CHB. Chinese J Pract Intern Med. 2006;26(11):845-846.
- Tkach S, Pankiv V, Krushinska Z. Features of type 2 diabetes combined with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver di–sease under conditions of chronic stress. Int J Endocrinol (Ukraine). 2024;20(1):18-24. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.20.1.2024.1353.
- Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang Y, et al. Hepatitis B patients exhibiting mild alanine aminotransferase elevation: A comparative analysis of treatment with and without bicyclol tablets. Biomed Rep. 2016;5(5):595-600. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.765.
- Zhao J, Chen H, Li Y. Histological changes in the liver in alcoholic liver disease during treatment with bicyclol and phosphatidylcholine: A comparative study. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 May 31;586(1–3):322-331.