Журнал «Травма» Том 26, №3, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Аналіз ревізійних хірургічних втручань на грудному та поперековому відділах хребта після транспедикулярної фіксації
Авторы: Барков О.О., Карпінська О.Д.
ДУ «Інститут патології хребта та суглобів ім. проф. М.І. Ситенка НАМН України», м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
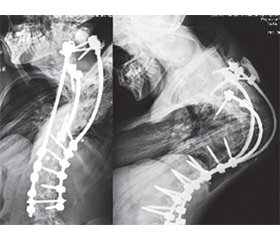
Актуальність. Операції на грудному та поперековому відділах хребта є важливими методами лікування широкого спектра патологій, але вони можуть супроводжуватися певними ризиками ускладнень, які суттєво впливають на результати лікування. Найбільш частими серед них є проблеми з імплантатами, захворювання суміжного сегмента, псевдоартроз чи інфекції. Деякі з них призводять до необхідності реоперації. Мета: на основі ретроспективних досліджень визначити основні види ревізійних втручань з приводу ускладнень після транспедикулярної фіксації грудного та поперекового відділів хребта. Матеріали та методи. Проведено ретроспективний аналіз 2128 історій хвороби пацієнтів, що лікувалися в ДУ «Інститут патології хребта та суглобів ім. проф. М.І. Ситенка НАМН України» з 2004 до 2018 року і яким було проведено транспедикулярну фіксацію хребта на грудному та поперековому відділах хребта. Серед них виявлено 268 пацієнтів, яким проведено ревізійні хірургічні втручання за різних причин. Проаналізовано ускладнення у 143 пацієнтів, пов’язані з транспедикулярною конструкцією, які включали проблеми з гвинтами (нестабільність, злам та некоректне проведення), стрижнями (нестабільність і злам) та комбіновані (нестабільність, злам стрижня та гвинтів). Результати. Визначено, що найбільш частими причинами для повторних втручань були ускладнення, пов’язані безпосередньо з транспедикулярною конструкцією (злам гвинтів, стрижнів, нестабільність конструкції, некоректне розташування гвинтів у хребці), у 143 (6,7 %) пацієнтів, залишковий біль після первинної операції спостерігали в 64 (3 %) пацієнтів. Інші ускладнення не перевищували 1 % від загальної кількості операцій. Основними ускладненнями були нестабільність та злам стрижнів, нестабільність та злам транспедикулярних гвинтів, нестабільність усіх компонентів конструкції та некоректне проведення гвинтів. Найбільшу кількість ускладнень відмічали після хірургічного лікування деформацій хребта — 21 (18,1 %). Другим за частотою ускладнень захворюванням був спондилолістез — 27 (8,8 %), при якому частіше спостерігали проблеми з гвинтами — 20 (6,51 %), враховуючи їх нестабільність — 14 (4,56 %) і некоректне розташування гвинтів — 6 (1,95 %). Висновки. За результатами проведеного дослідження загальний рівень ускладнень після транспедикулярної фіксації, які призвели до ревізійних втручань, становив 12,6 %. Визначено, що найбільш частими причинами для повторних втручань були ускладнення, пов’язані з транспедикулярною конструкцією (злам гвинтів, стрижнів, нестабільність конструкції, некоректне розташування гвинтів у хребці), у 143 (6,7 %) пацієнтів. Другим за поширеністю ускладненням був залишковий біль (faildback-синдром) після первинно виконаної інструментації хребта, що відмічався у 64 пацієнтів (3,0 %). Інші ускладнення не перевищували 1 % від загальної кількості операцій.
Background. Surgery on the thoracic and lumbar spine is an important method of treating a wide range of pathologies, but it can be accompanied by certain risks of complications that significantly affect treatment outcomes. The most common of these are problems with implants, diseases of the adjacent segment, pseudoarthrosis, or infections. Some of them lead to the need for reoperation. The purpose was based on retrospective studies, to determine the main types of revision interventions for complications after transpedicular fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis was conducted of 2,128 medical records of patients who were treated at the Sytenko Institute of Spine and Joint Pathology of NAMSU from 2004 to 2018 and underwent transpedicular fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Among them, 268 patients were identified who underwent revision surgery for various reasons. Complications associated with transpedicular construction, including problems with screws (instability, fracture, and incorrect placement), rods (instability and fracture), and combined problems (instability, fracture of the rod and screws) were analyzed in 143 patients. Results. It was found that the most common reasons for repeat interventions were complications directly related to the transpedicular structure (fracture of screws, rods, instability of the construction, incorrect placement of screws in the vertebra) in 143 (6.7 %) patients. Residual pain after the initial surgery was observed in 64 (3 %) interventions. Other complications did not exceed 1 % of the total number of surgeries. The main complications were instability and fracture of rods, instability and fracture of transpedicular screws, instability of all components of the structure, and incorrect placement of screws. The highest number of complications was observed after surgical treatment for spinal deformities — 21 (18.1 %). The second most frequent complication was spondylolisthesis — 27 (8.8 %), in which problems with screws were more common — 20 (6.51 %), including their instability — 14 (4.56 %) and incorrect screw placement — 6 (1.95 %). Conclusions. According to the results of the study, the overall rate of complications after transpedicular fixation that led to revision surgery was 12.6 %. It was found that the most common reasons for repeat interventions were complications related to the transpedicular construction (fracture of screws, rods, instability of the structure, incorrect placement of screws in the vertebra) in 143 (6.7 %) patients. The second most common complication was residual pain (“failed back” syndrome) after the initial spinal instrumentation, which accounted for 64 (3.0 %) cases. Other complications did not exceed 1 % of the total number of operations.
транспедикулярна фіксація; ускладнення; спондилолістез; деформації хребта; травма хребта
transpedicular fixation; complications; spondylolisthesis; spinal deformities; spinal injury